Qwen-VL系列
Qwen-VL
阿里巴巴的Qwen-VL是另一个比较经典的模型,十分值得作为案例介绍多模态大模型的训练要点。Qwen-VL使用Qwen-7B LLM作为语言模型基座,Openclip预训练的ViT-bigG作为视觉特征Encoder,随机初始化的单层Cross-Attention模块作为视觉和自然语言的的Adapter,总参数大小约9.6B。
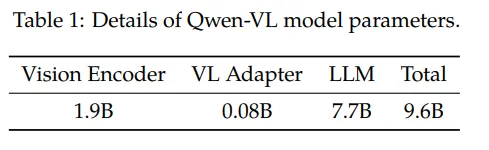
如下图,Qwen-VL的训练过程分为三个阶段:
- Stage1 为预训练,目标是使用大量的图文Pair对数据对齐视觉模块和LLM的特征,这个阶段冻结LLM模块的参数;
- Stage2 为多任务预训练,使用更高质量的图文多任务数据(主要来源自开源VL任务,部分自建数据集),更高的图片像素输入,全参数训练;
- Stage3 为指令微调阶段,这个阶段冻结视觉Encoder模块,使用的数据主要来自大模型Self-Instruction方式自动生成,目标是提升模型的指令遵循和多轮对话能力。
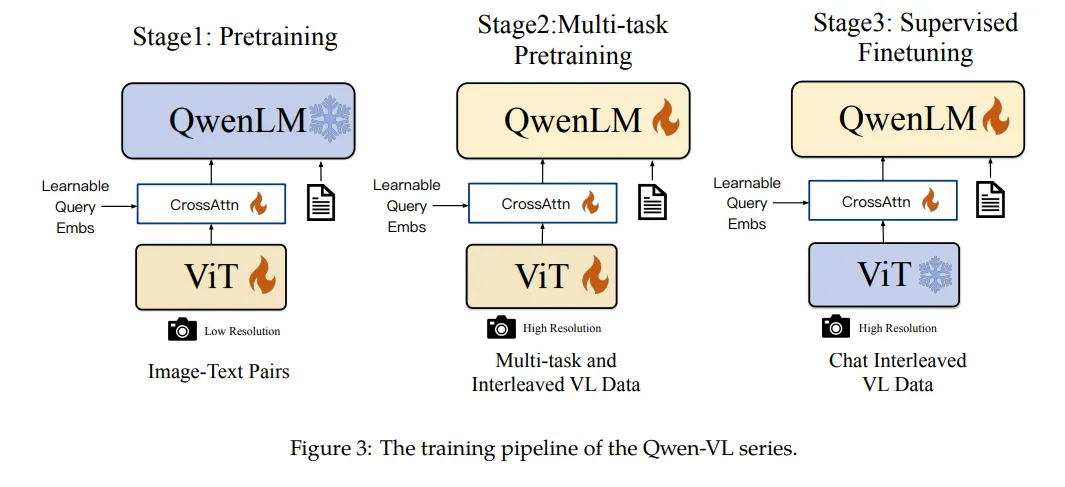
Qwen-VL的另一个启发是在Stage2和Stage3的训练过程中,不止使用VL数据,还使用了纯文本的训练数据,避免遗忘LLM的能力,这个策略的效果在其他的工作中也有所印证。此外,相比InstructBLIP,Qwen-VL模型视觉和LLM的Adapter模块简化很多,仅仅是一个浅层的Attention Pooling模块,通过更加细节的训练流程和更加丰富的训练数据,仍取得了比InstructBLIP更优的效果。
Qwen2-VL
Qwen2-VL 基于 Qwen2 打造,相比 Qwen-VL,它具有以下特点:
- 读懂不同分辨率和不同长宽比的图片:Qwen2-VL 在 MathVista、DocVQA、RealWorldQA、MTVQA 等视觉理解基准测试中取得了全球领先的表现。
- 理解20分钟以上的长视频:Qwen2-VL 可理解长视频,并将其用于基于视频的问答、对话和内容创作等应用中。
- 能够操作手机和机器人的视觉智能体:借助复杂推理和决策的能力,Qwen2-VL 可集成到手机、机器人等设备,根据视觉环境和文字指令进行自动操作。
- 多语言支持:为了服务全球用户,除英语和中文外,Qwen2-VL 现在还支持理解图像中的多语言文本,包括大多数欧洲语言、日语、韩语、阿拉伯语、越南语等。
整体上我们仍然延续了 Qwen-VL 中 ViT 加 Qwen2 的串联结构,在三个不同尺度的模型上,我们都采用 600M 规模大小的 ViT,并且支持图像和视频统一输入。为了让模型更清楚地感知视觉信息和理解视频,我们还进行了以下升级:
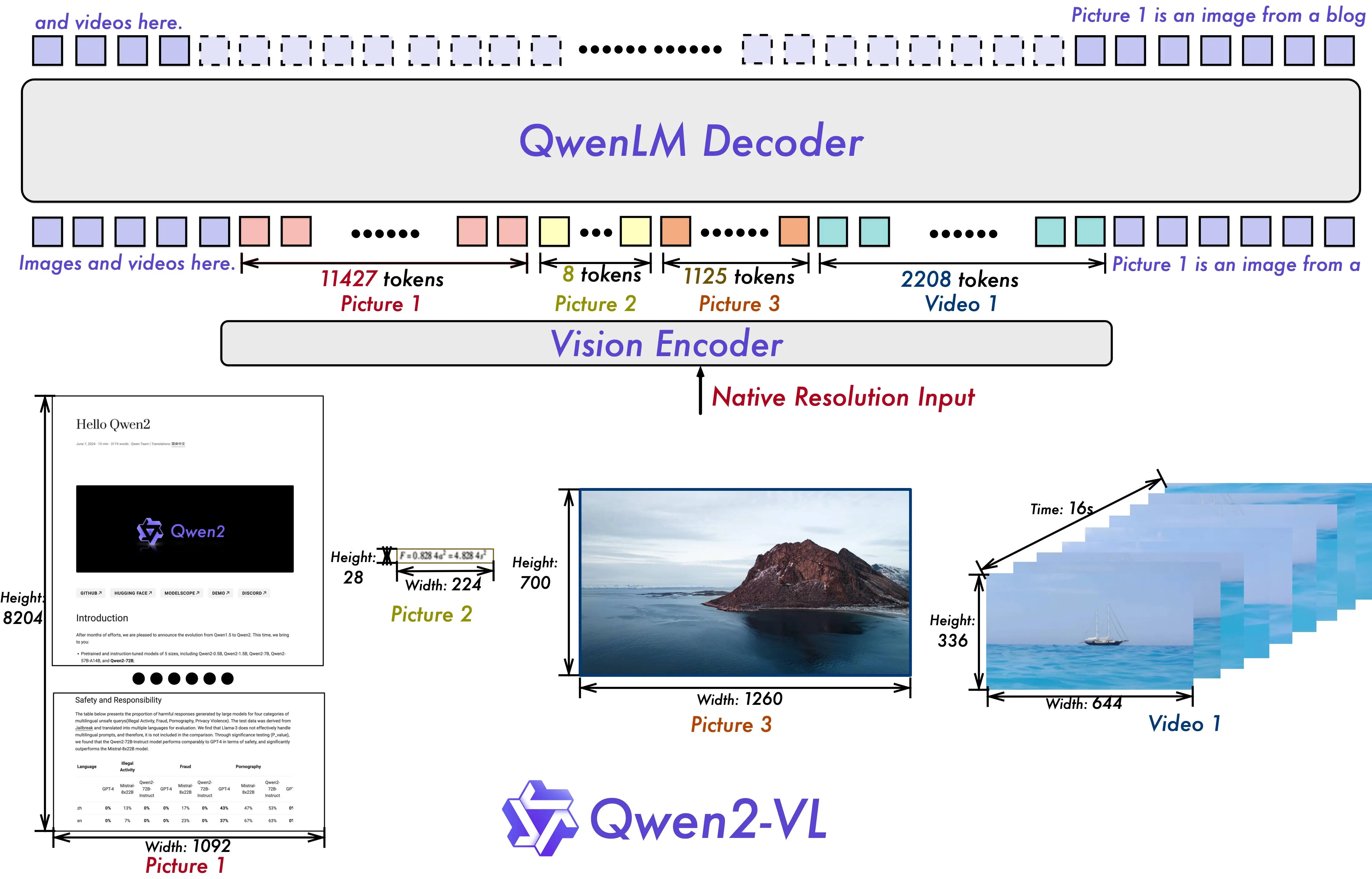
- Qwen2-VL 在架构上的一大改进是实现了对原生动态分辨率的全面支持。与上一代模型相比,Qwen2-VL 能够处理任意分辨率的图像输入,不同大小图片被转换为动态数量的 tokens,最小只占 4 个 tokens。这种设计不仅确保了模型输入与图像原始信息之间的高度一致性,更是模拟了人类视觉感知的自然方式,赋予模型处理任意尺寸图像的强大能力,使其在图像处理领域展现出更加灵活和高效的表现。实现的方式就是用
Navit作为visual的encoder以及苏神的2D-RoPE - Qwen2-VL 在架构上的另一重要创新则是多模态旋转位置嵌入(M-ROPE)。传统的旋转位置嵌入只能捕捉一维序列的位置信息,而 M-ROPE 通过将原始旋转嵌入分解为代表时间、高度和宽度的三个部分,使得大规模语言模型能够同时捕捉和整合一维文本序列、二维视觉图像以及三维视频的位置信息。这一创新赋予了语言模型强大的多模态处理和推理能力,能够更好地理解和建模复杂的多模态数据
Qwen2.5-VL
Qwen2.5-VL 的主要特点如下所示:
- 感知更丰富的世界:Qwen2.5-VL 不仅擅长识别常见物体,如花、鸟、鱼和昆虫,还能够分析图像中的文本、图表、图标、图形和布局。
- Agent:Qwen2.5-VL 直接作为一个视觉 Agent,可以推理并动态地使用工具,初步具备了使用电脑和使用手机的能力。
- 理解长视频和捕捉事件:Qwen2.5-VL 能够理解超过 1 小时的视频,并且这次它具备了通过精准定位相关视频片段来捕捉事件的新能力。
- 视觉定位:Qwen2.5-VL 可以通过生成 bounding boxes 或者 points 来准确定位图像中的物体,并能够为坐标和属性提供稳定的 JSON 输出。
- 结构化输出:对于发票、表单、表格等数据,Qwen2.5-VL 支持其内容的结构化输出,惠及金融、商业等领域的应用。
Qwen3-VL
25年9月,正式推出全新升级的 Qwen3-VL 系列——这是迄今为止 Qwen 系列中最强大的视觉语言模型。
在这一代模型中,我们在多个维度实现了全面跃升:无论是纯文本理解与生成,还是视觉内容的感知与推理;无论是上下文长度的支持能力,还是对空间关系、动态视频的理解深度;乃至在与Agent交互中的表现,Qwen3-VL 都展现出显著进步。
率先开源的是该系列的旗舰模型 —— Qwen3-VL-235B-A22B,同时包含 Instruct 与 Thinking 两个版本。其中,Instruct 版本在多项主流视觉感知评测中,性能达到甚至超过 Gemini 2.5 Pro;而 Thinking 版本更是在众多多模态推理的评测基准下取得了 SOTA 的表现。
Qwen3-VL 的目标,是让模型不仅能“看到”图像或视频,更能真正看懂世界、理解事件、做出行动。主要的升级如下:
- 视觉智能体(Visual Agent):Qwen3-VL 能操作电脑和手机界面、识别 GUI 元素、理解按钮功能、调用工具、执行任务,在 OS World 等 benchmark 上达到世界顶尖水平,能通过调用工具有效提升在细粒度感知任务的表现。
- 纯文本能力媲美顶级语言模型:Qwen3-VL 在预训练早期即混合文本与视觉模态协同训练,文本能力持续强化,最终在纯文本任务上表现与 Qwen3-235B-A22B-2507 纯文本旗舰模型不相上下 —— 是真正“文本根基扎实、多模态全能”的新一代视觉语言模型。
- 视觉 Coding 能力大幅提升:实现图像生成代码以及视频生成代码,例如看到设计图,代码生成 Draw.io/HTML/CSS/JS 代码,真正实现“所见即所得”的视觉编程。
- 空间感知能力大幅提升:2D grounding 从绝对坐标变为相对坐标,支持判断物体方位、视角变化、遮挡关系,能实现 3D grounding,为复杂场景下的空间推理和具身场景打下基础。
- 长上下文支持和长视频理解:全系列模型原生支持 256K token 的上下文长度,并可扩展至 100 万 token。这意味着,无论是几百页的技术文档、整本教材,还是长达两小时的视频,都能完整输入、全程记忆、精准检索,支持视频精确定位到秒级别时刻。
- 多模态思考能力显著增强:Thinking 模型重点优化了 STEM 与数学推理能力。面对专业学科问题,模型能捕捉细节、抽丝剥茧、分析因果、给出有逻辑、有依据的答案,在 MathVision、MMMU、MathVista 等权威评测中达到领先水平。
- 视觉感知与识别能力全面升级:通过优化预训练数据的质量和广度,模型现在能识别更丰富的对象类别——从名人、动漫角色、商品、地标,到动植物等,覆盖日常生活与专业领域的“万物识别”需求。
- OCR 支持更多语言及复杂场景:支持的中英外的语言从 10 种扩展到 32 种,覆盖更多国家和地区;在复杂光线、模糊、倾斜等实拍挑战性场景下表现更稳定;对生僻字、古籍字、专业术语的识别准确率也显著提升;超长文档理解和精细结构还原能力进一步提升。
关于QwenVL系列,详情可以查看:QwenVL 系列
LLaVA
LLaVA 1.5
同样,微软的LLaVA也是一个持续更新的系列工作,这里主要总结LLaVA和LLaVA1.5的核心思路。下图为LLaVA1.5的数据和模型概况。可以看到,和Qwen-VL相比,LLaVA1.5在预训练和指令微调数据上使用了更少的数据(将Qwen-VL的Stage2和Stage3都视作指令微调);在模型结构上,除了视觉Encoder和LLM均使用了不同的基座模型,视觉和自然语言的Adapter使用更简单的MLP层。
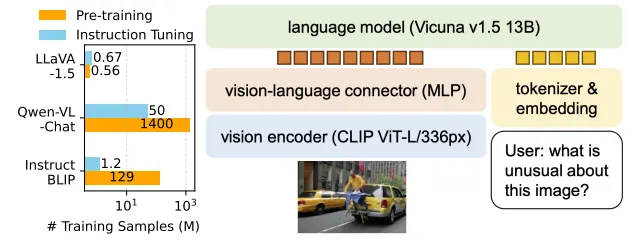
LLaVA1.5模型的效果在一些评测数据集上相比Qwen-VL有更好的效果,说明通过一些优化工作,使用更少的数据,更简单的Adapter结构,也能使LLM具备不错的多模态理解能力。在数据层面,对比LLaVA1.5和LLaVA工作,通过增加高质量细粒度的VL数据、丰富指令、纯文本指令微调数据、提升图片输入像素、提升LLM参数规模等手段,可以有效提升模型效果。
LLaVA-Onevison
Onevision整合了在 LLaVA-NeXT(llava 1.5) 中对数据、模型和视觉表示的见解。实验结果表明,LLaVA-OneVision 是第一个能够在三个重要计算机视觉场景(单图像、多图像和视频场景)中同时推动开放 LMM 性能边界的模型。重要的是,LLaVA-OneVision 的设计允许跨不同模态/场景进行强大的迁移学习,从而产生新的涌现能力。特别是,通过从图像到视频的任务迁移,展示了强大的视频理解和跨场景能力。
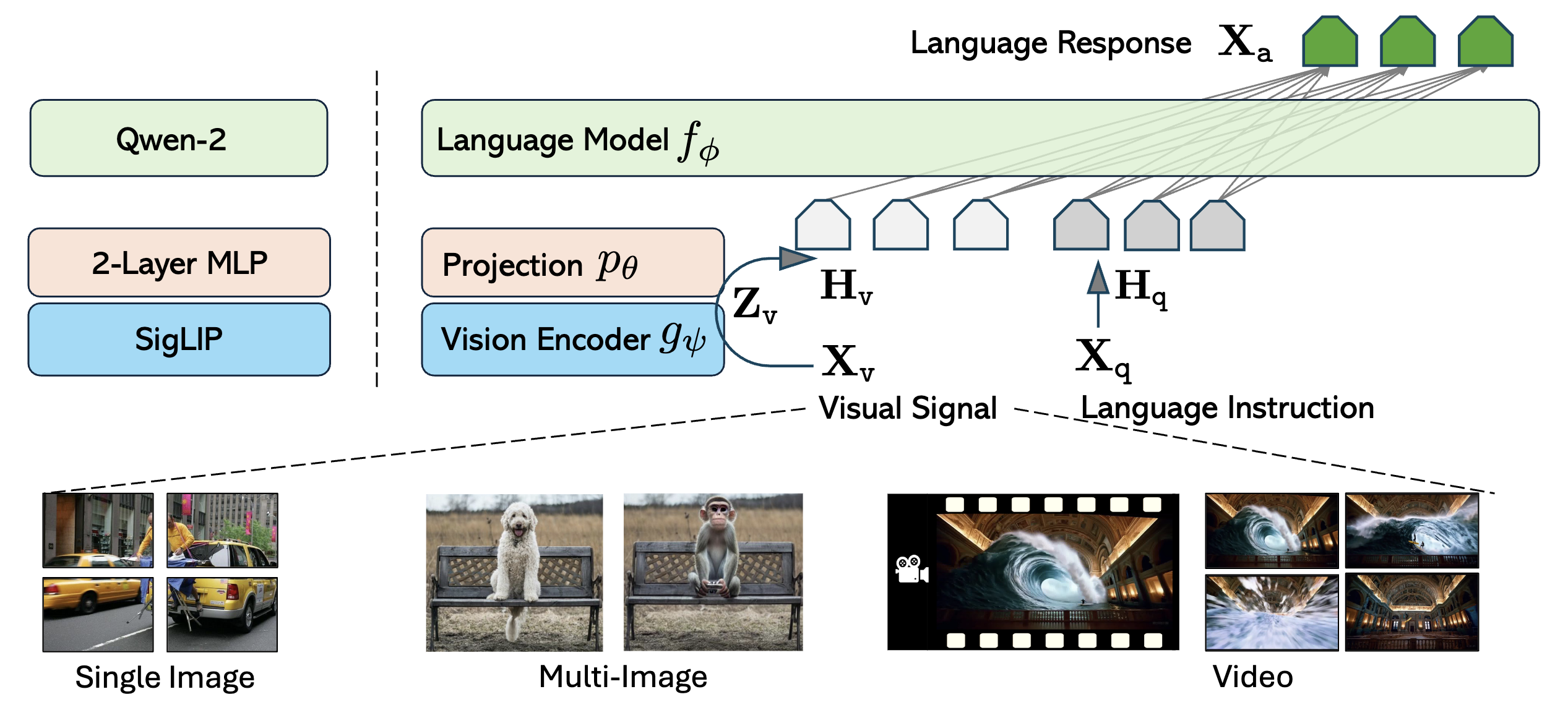
这里直接先放出onevistion整体的训练策略
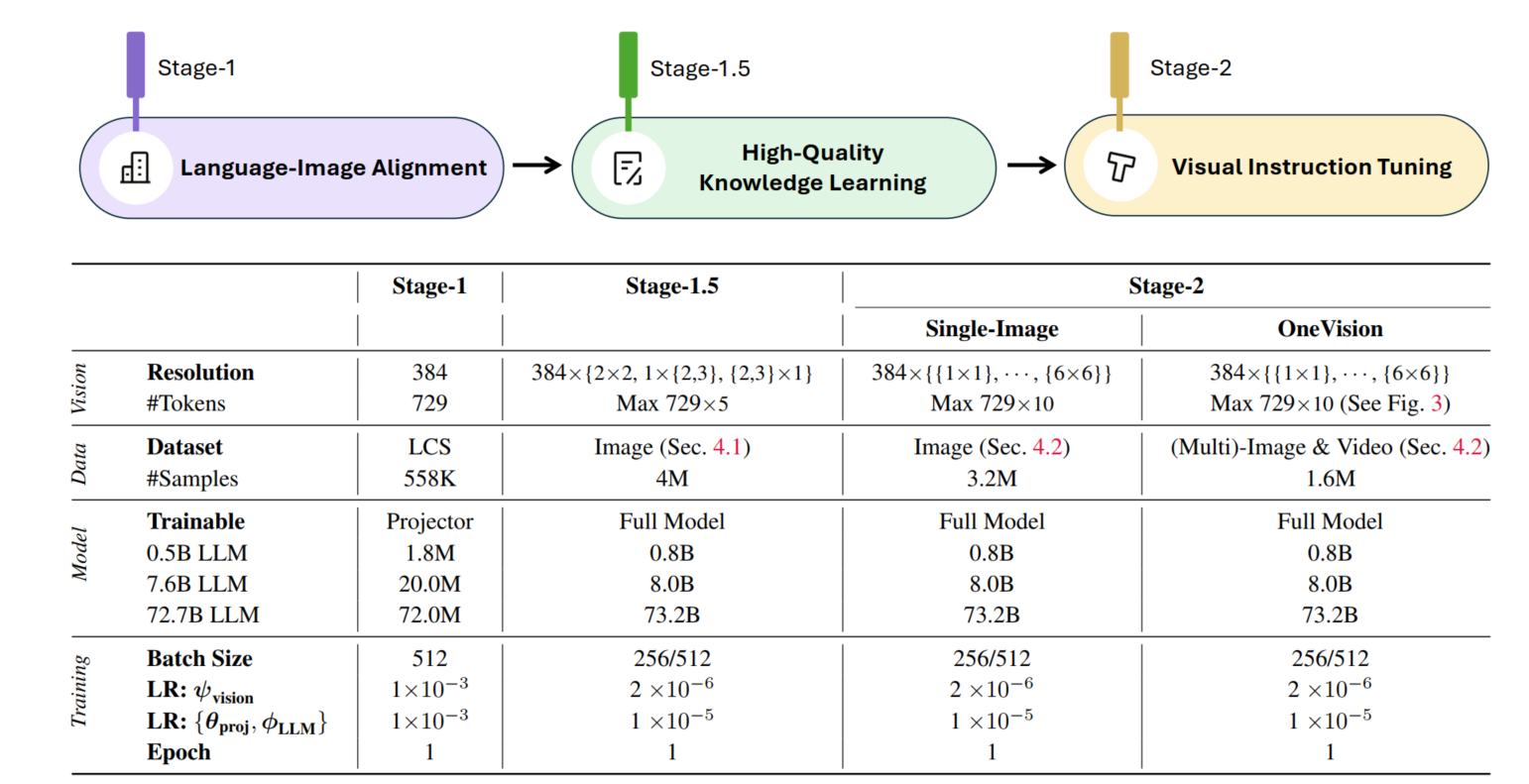
LLaVA-OneVisoion-1.5
LLaVA-OneVision-1.5 是一个全开源的模型,包括代码,数据,模型。这次的升级主要包含三大核心组件:
- 大规模精选数据集:构建了含 8500 万条概念平衡预训练数据的数据集 LLaVA-OneVision-1.5-MidTraning,以及经精心整理、含 2200 万条指令数据的数据集 LLaVA-OneVision-1.5-Instruct;
- 高效训练框架:开发了完整的端到端高效训练框架,采用离线并行数据打包策略,确保可在 1.6 万美元预算内完成 LLaVA-OneVision-1.5 的训练;
- 最先进性能:实验结果表明,LLaVA-OneVision-1.5 在各类下游任务中均展现出极具竞争力的性能。
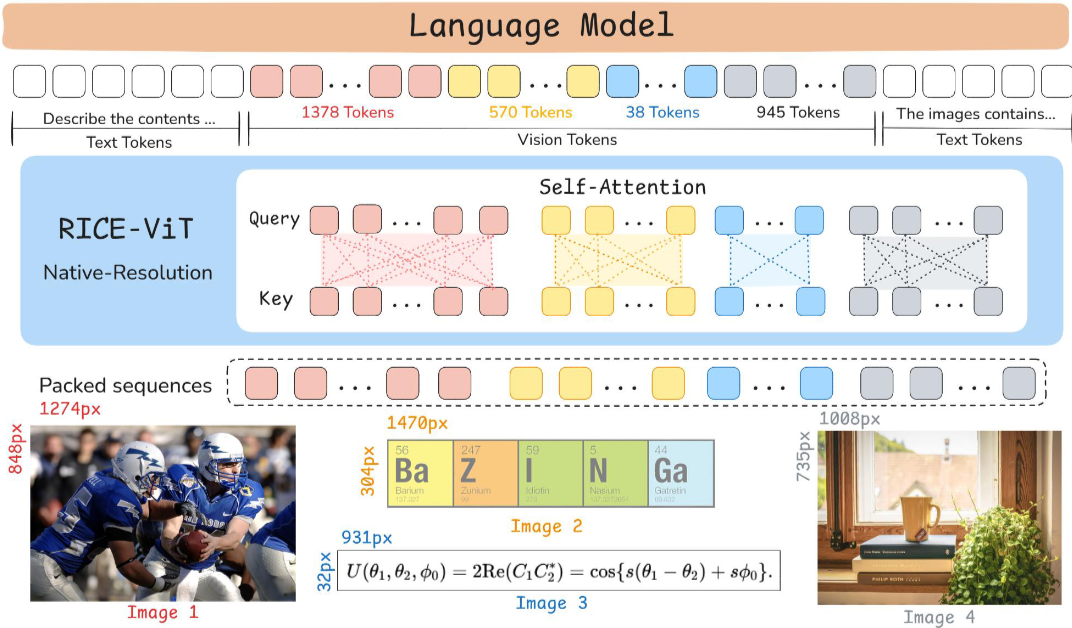
LLaVA-OneVision-1.5 的整体架构如上图所示。该模型沿用 LLaVA 系列的 “ViT(视觉 Transformer)-MLP(多层感知机)-LLM(大型语言模型)” 范式,包含三大核心模块:
- 视觉编码器(Vision Encoder):视觉编码器负责从输入图像中提取丰富且具有语义意义的视觉表征,为多模态对齐与下游推理奠定基础。与以往采用 SigLIP或 DFN,LLaVA-OneVision-1.5 整合了近期提出的聚类判别模型 RICE-ViT,以提升区域感知视觉能力与光学字符识别(OCR)能力。
- 投影层(Projector):投影层通过将视觉嵌入映射至大型语言模型(LLM)的文本嵌入空间,弥合视觉编码器与大型语言模型之间的模态鸿沟。参考 Qwen2.5-VL的设计,首先对空间上相邻的四组图像块特征进行分组,随后将其拼接并输入一个两层多层感知机(MLP),最终映射至大型语言模型的文本嵌入空间。
- 大型语言模型(Large Language Model):大型语言模型是该架构的推理与生成核心。在接收投影后的多模态嵌入后,大型语言模型将视觉信息与语言上下文融合,以执行复杂推理、指令跟随与自然语言生成任务。LLaVA-OneVision-1.5 系列模型采用 Qwen3作为语言骨干网络,大幅提升下游任务的性能。
llava系列的具体细节参考:LLaVA系列
VILA
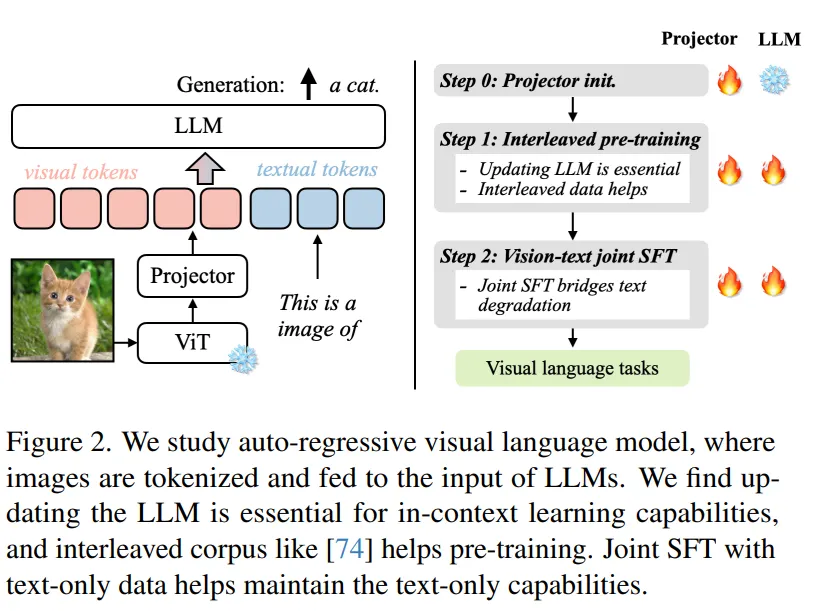
另一个与LLaVA比较类似,但有所补充的工作是英伟达的VILA(不是显卡)。VILA模型的网络结构和LLaVA十分类似,我们不做过多赘述。不同的是VILA通过实验,总结了多模态预训练的一些经验,其中有些经验在相关工作中也有所体现,主要为以下三点:
- LLM参与训练更好:在预训练阶段冻结LLM参数,能做到不错的zero-shot的能力,但会损失in-context学习的能力,而LLM参数参与训练的话可以有效缓解;
- 预训练数据使用图文交替数据更好:图文Pair对并不是最优的选择,图文交错的数据效果更好;

- SFT时纯文本数据图文数据混合更好:在图文指令微调训练数据中混入纯文本的指令数据,不仅可以缓解纯文本能力的遗忘,还能提升VL任务的能力。
具体的,如下图,VILA的训练分为3个阶段,视觉编码模块ViT参数均是冻结状态。Step 0 使用图文Pair数据对初始化Projector(图文Adapter)参数,LLM模块参数冻结;Step 1使用图文交替数据全参数预训练;Step 2使用指令微调数据进行全参数微调,其中微调数据混合了图文指令和纯文本指令;
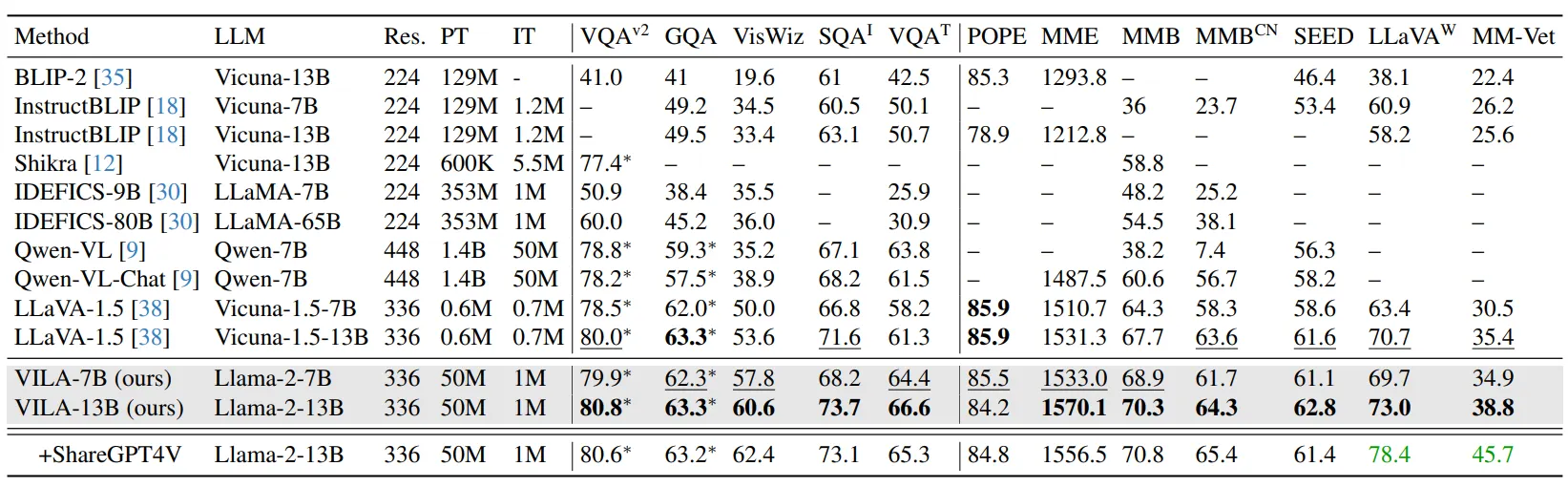
VILA相对各时期的SoTA,在公开评测指标上有不错的效果, 如下图。
Gemini
目光来到闭源世界,与VILA同阶段,谷歌公司发布了Gemini系列,又在近期发布了性能更强的Gemini 1.5,可惜被另一个热爱闭源的OpenAI的Sora抢了风头,属实悲催。由于Gemini系列并没有开源,我们只能通过技术报告中的简单介绍来了解其方法。
Gemini 1.0是一个多模态模型,这里模态除了图图像和文还包括音频、视频,符合谷歌多模态大模型一贯的ALL IN ONE的风格,这也是依赖积累丰富的数据资源和算力资源。Gemini 1.0提供Ultra、Pro和Nano版本,分别适应不同能力、参数大小和推理速度要求,最小的Nano甚至可以端上运行。
方法上,Gemini 1.0的网络结构同样是Transformer Decoders,支持32K上下文长度,使用了Multi-Query Attention等优化机制。如图,模型输入可以是文本、音频、视觉输入,输入视觉可以是图片、图表、截图、PDFs或视频等,输出可以是图片和文本(没错,可以生成图片)。视觉的Encoder模块借鉴了谷歌自己的Flamingo、CoCa和PaLI,结合这些模型,可以输入多模态的同时,也可以通过离散的视觉Tokens生成图片或视频等视觉模态。
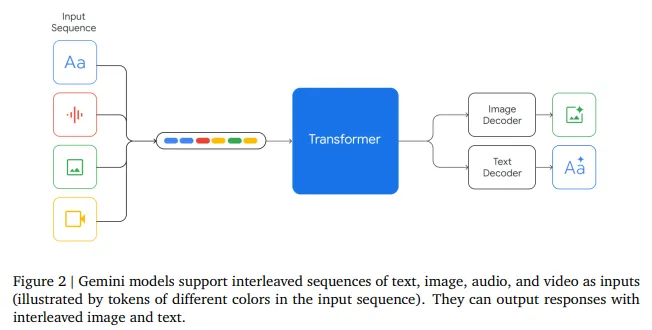
对于音频模态,Gemini可以直接输入Universal Speech Model (USM)的16kHz特征,具体可以参考USM工作。对于视频理解,Gemini通过将视频编码为长上下文窗口中的一系列帧来实现。视频帧或图像可以与文本或音频自然交织在一起,作为模型输入的一部分。Gemini同时支持不同像素输入的视觉以满足不同粒度的理解任务。
在具体训练数据方面,技术报告同样并没有提过多细节,只是简单说了数据包括什么模态、经过了什么清洗步骤等,我们也不再深究。至于Gemini 1.5,同样是技术报告的形式发布,没有特别多技术细节,主要介绍了模型是如何的强。区别要点包括:模型在Gemini 1.0基础上引入了sparse mixture-of-expert (MoE),同时强化了上下文长度(32K->10M)同时几乎没有损失上下文感知能力。在训练过程中,Gemini 1.5强化了指令微调过程,使用了用户偏好数据。
总体来说,虽然Gemini没有提供技术细节,但也体现了谷歌对于多模态大模型技术方向的判断,比如我们可以get到网络结构的MoE、一个模型更多模态、超长上下文、文本生成+多模态生成结合等。
Mini-Gemini
TL; DR:本文构建了一个支持 text+image 多模态输入、text+image 多模态输出的真正的多模态大模型 Mini-Gemini。技术方面主要有三个要点:
- 高效高分辨率的视觉 token 编码,
- 高质量的数据,
- 通过 VLM 引导的图像生成。
现有的多模态大模型一般支持文本和图片输入,但支持输出文本回复。像 Gemini / GPT4+DALLE3 那样支持多模态输出的模型不多。本文通过高分辨率的视觉 token,高质量的数据,以及通过 VLM 引导的图像生成三个方面的技术改进,构建一个支持图文输入、图文输出的多模态大模型 Mini-Gemini 系列。整体框架如下图所示。
高分辨率的视觉 token
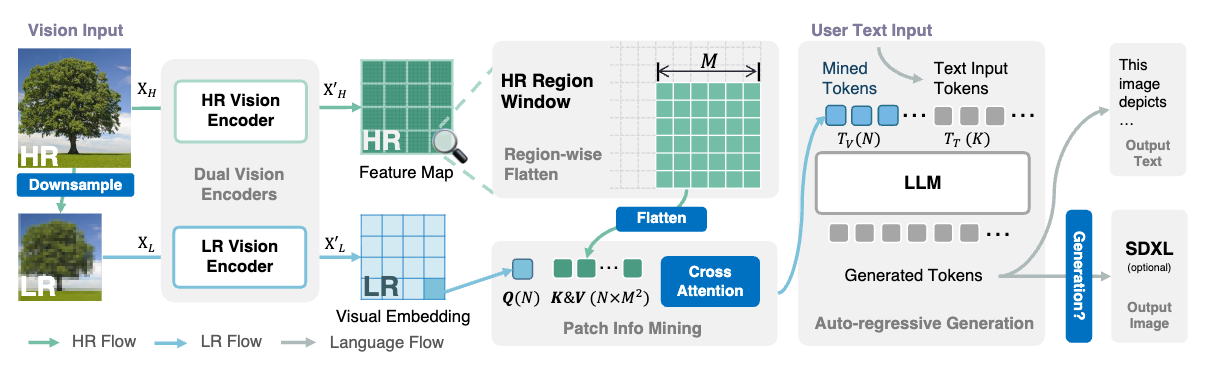
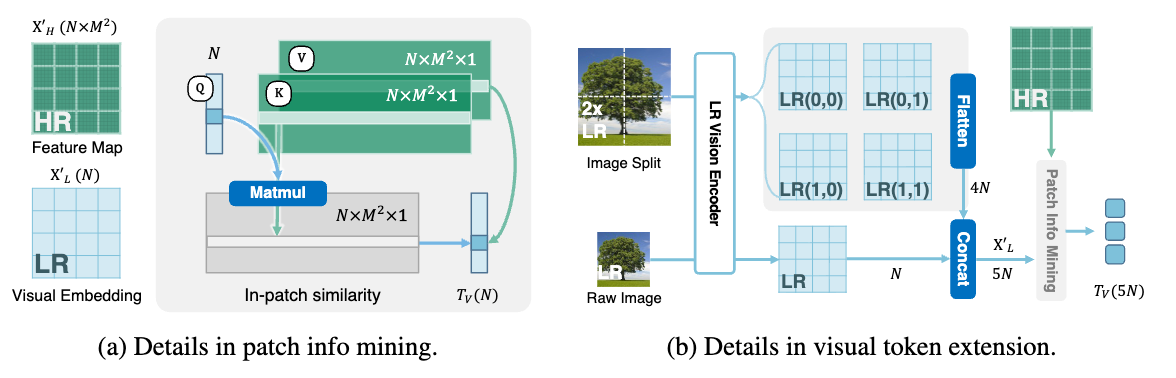
支持高分辨率图像理解、文档文字图理解,是近来新发布的多模态大模型重点在卷的一个能力。像 LLaVA 1.6 的图片切分方案,Fuyu 的纯 Decoder 方案等都在这方面有所优化。Mini-Gemini 提出了一种新的高分辨率图像理解的优化方案。Mini-Gemini 中使用了 Conv 和 ViT 两种视觉编码器,分别编码高分辨率和低分辨率的图像信息,然后提出一种图像块信息挖掘(patch info mining)的方法,将低分辨率视觉 tokens 作为 Query,高分辨率的视觉 tokens 作为 Key 和 Value,进行交叉注意力操作,再输入到 LLM 中作为视觉 token。
这么做的原因是,低分辨率图像经过 ViT 提取的 tokens 是某个图像块的信息,而高分辨率经过 Conv 提取的特征图也是不同区域的图像特征,如此进行交叉注意力操作,使得每个 query 在其对应的子区域中有较高的注意力值。并且,最终输出的视觉 token 个数也是固定的,不会将高分低分所有的视觉 token 都输入到 LLM 中,计算开销较低。基于这种 dual-encoder + patch info mining 的方案,能够保持图像的细节信息,并且编码过程比较高效。
另外,如果需要更细节的对图像细节的理解,该方法还可以扩展为更高清的版本。具体操作是,在低分编码分支,先将原图长宽各进行两倍上采样并切分,这样最终得到 5 倍于原方案的低分辨率像素数,并最终的视觉 token 数也是 5 倍。
多模态生成
经过上述方案进行高效的高分辨率图像编码后,将视觉 token 和文本 token 拼接并输入到 LLM 中,进行自回归式的生成。不同于大多数仅有文本单模态输出形式的 VLM,Mini-Gemini 还支持图像的生成。现有支持图像生成的多模态大模型,一般是训练模型对齐 LLM 和 Diffusion Model 的文本 embedding,而本文中 Mini-Gemini 则是训练 LLM 理解用户的生图指令,并输出适合 Diffusion Model 生图的 prompt,然后调用现成的 SD 等生图模型,实现图像生成。
高质量数据
高质量的数据,是如今训练 LLM 最重要的因素。
常规的 VLM 数据部分包括文本、多模态的指令数据,文档数据,OCR 数据等。
另一部分很关键的是生图训练数据。Mini-Gemini 的生图方案需要 LLM 能够理解用户的生图意图,并改写、润色出一个适合 SD 模型进行生图的文本 prompt。
如下图所示,这部分训练数据包含两个任务:(a)简单指令 recaption:采用 LAION-GPT-4V 中的 8K 详细描述性图像 caption,并让 GPT-4 反推相应用户的简短图像 caption 输入和适用于 SD 的生图 prompt。 (b) 上下文提示生成:基于 LIMA 和 OpenAssistant2 中的一些高质量的真实对话上下文,生成 prompt 和符合对话上下文的图像,共得到 5K 条指令数据。 为了格式化地出发生图,Mini-Gemini 使用特殊 token <GEN> 来标识本轮对话需要调用 SD 进行生图,用特殊 token <h>...</h> 来包裹 LLM 改写出的生图 prompt,送入 SD 中。

Mini-Gemini 通过 LLM 显式地改写出生图 prompt,并外挂 SDXL 进行图像生成,不同于之前直接嫁接 text embedding 的方案,实测效果还不错。更重要的是,生成自然语言生图的 prompt 具有更好的灵活性和可解释性,可以无缝接入其他的生图模型。另外笔者还有一个想法,能否将输入的图片通过 ip-adapter 等方式也作为生图的条件,从而实现定制化生图等。
高分辨率的编码方法来理解图像细节和文字图等,也是一个技术改进,最近很多新发布 VLM 在做类似的工作。
InternVL
InterVL系列发力比QwenVL系列更早,并且一直保持开源的风格。尤其是Qwen1-VL到Qwen2-VL将近一年的空窗期中,InternVL从1.0,1.1,1.2,1.5一直高速迭代,所以,从InternVL身上,我们更能看得出来国内VL社区从BLIP时代到LLM时代的发展路线。简单做个重点梳理(忽略数据改变):
- InternVL 1.0 就是BLIP时代的产物,大家还没有思考清楚 对比 & 生成 应该如何交融,才能训练出理解能力和生成能力都非常强的VLM,另外就是InternVL团队之前和zhiyuan团队一样,都在押注大视觉模型,因此视觉端还比较重。
- InternVL 1.1 和 InternVL 1.2 按照LLaVA的模式,去掉Q-fomer这种重的adapter组建,改为MLP,并且三阶段训练简化为两阶段训练。
- InternVL 1.5接入动态分辨率处理
- InternVL 2 接入视频输入、医疗图像输入,8B及以下模型舍弃6B的视觉encoder改为300M ViT
- InternVL 2.5 引入double数据、使用CoT(原文称作Test-Time Scaling,但是没有RL的Test-Time Scaling都是伪Test-Time Scaling)取得了更好的性能
- InternVL 3 集成了可变视觉位置编码(V2PE)、优化多模态预训练方式,并引入了MPO作为后训练从而提高推理性能
- InternVL 3.5 加入了视觉分辨率路由器(实现视觉标记的自适应压缩,每个图像块会根据其语义丰富程度被路由到合适的压缩率),并进一步增强了后训练流程,提出级联强化学习渐进式训练(MPO+GSPO)
具体详情参考:InternVL系列
MiniCPM-V
MiniCPM-V 端侧多模态大模型系列可以以端到端方式,接受图像、视频、文本、音频作为输入,并生成高质量文本和语音输出。MiniCPM-o 进一步支持端到端的语音输入输出。自2024年2月以来,我们以实现高性能和高效部署为目标,发布了7个版本的模型。目前系列中最值得关注的模型包括:
- MiniCPM-V 4.5:MiniCPM-V 系列中最新、最强大的模型。总参数量 8B,在视觉能力上超越了 GPT-4o-latest、Gemini-2.0 Pro 以及 Qwen2.5-VL 72B,成为开源社区中性能最强的端侧多模态模型。本版本带来了全新特性,包括高效的高帧率与长视频理解(视频 token 压缩率最高可达 96 倍)、可控的快思考/深思考模式、出色的手写体 OCR 与复杂表格/文档解析能力。同时,它进一步强化了 MiniCPM-V 系列广受欢迎的特性,如可靠性、多语言支持与端侧可部署性。
- MiniCPM-o 2.6: MiniCPM-o 系列中性能最佳模型。总参数量 8B,视觉、语音和多模态流式能力达到了 GPT-4o-202405 级别,是开源社区中模态支持最丰富、性能最佳的模型之一。在新的语音模式中,MiniCPM-o 2.6 支持可配置声音的中英双语语音对话,还具备情感/语速/风格控制、端到端声音克隆、角色扮演等进阶能力。模型也进一步提升了 MiniCPM-V 2.6 的 OCR、可信行为、多语言支持和视频理解等视觉能力。基于其领先的视觉 token 密度,MiniCPM-V 2.6 成为了首个支持在 iPad 等端侧设备上进行多模态实时流式交互的多模态大模型。
详情查看:MiniCPM-V系列
NVLM
https://research.nvidia.com/labs/adlr/NVLM-1/
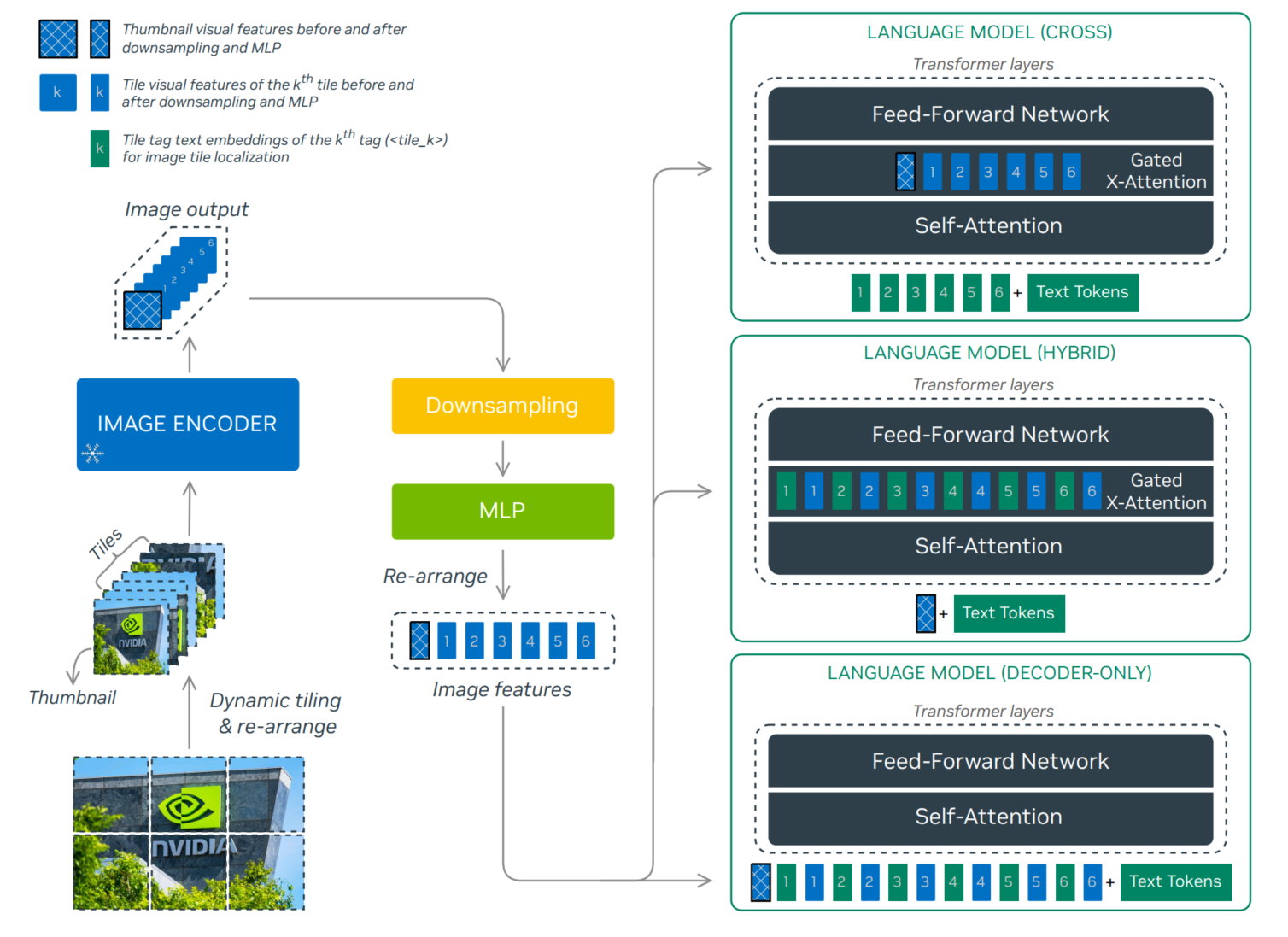
- NVLM-D: Decoder-only Model: 上图下边结构,图像和文本拼接用LLM做decoder(和常见的VLM结构相同),并加入1-D flattened tile tag:
<tile_1>,<tile_2>, · · · ,<tile_6>,<tile_global>. - NVLM-X: X-attention Model: 上图上边结构,图像和文本在Gated X-Atention做cross attention(类似Flamingo),同样加入1-D flattened tile tag
- NVLM-H: Hybrid Model :融合X和D,只将缩略图和text送入LLM, 同样加入Gated X-Atention,用其他图像tail和self-attention之后的特征做cross Attention
Ovis
https://github.com/AIDC-AI/Ovis/tree/main
整体模型结构如图所示
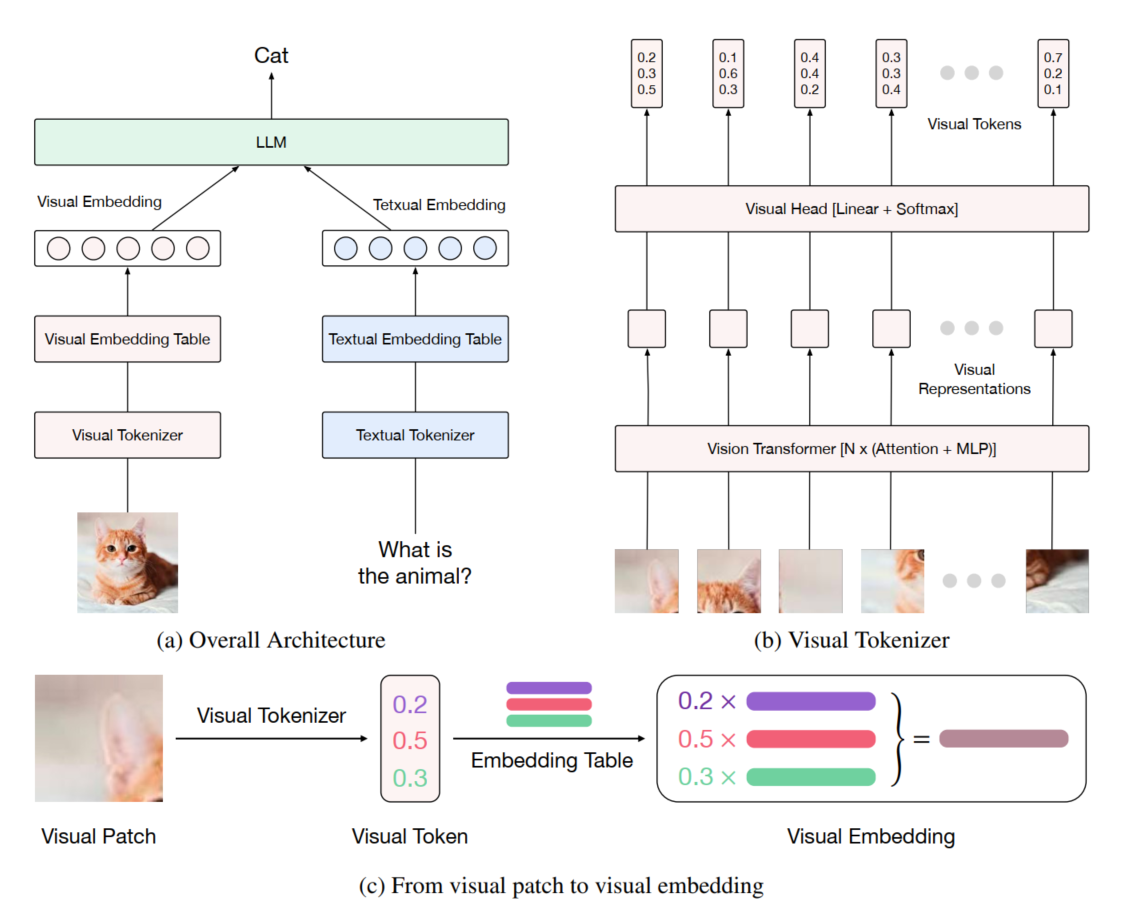
之前的方法在对齐离散的text特征(对应为一维token embeding)和visual 特征(对应为二维离散特征序列,patches embeding)时,二者的维度不同,所以基本都是采用比较简单的方法去对齐,比如llava就是将视觉特征再通过MLP将其转换为一维的视觉特征序列,再将二者合并后送入LLM进行训练。
Ovis的做法是,将视觉离散化,统一为和文本特征统一的形式,也就是对齐到一个统一的空间再做对齐。具体为,给定一个视觉token \(r_i \in \mathbb{R}^d\) (可以理解为通过VIT提取的一个patch特征),通过
视觉嵌入表(Visual Embedding Table)
每个视觉单词 \(w_i \)作为一个原型(prototype),存储在嵌入表中,形式为 \( \{w_i \in \mathbb{R}^d\}_{i=1}^K\),其中\(K\)为词典的大小,也就代表了视觉词典中包含有\(K\)个独特的视觉单词,
匹配机制
为了将连续的视觉token \(r_i \)与嵌入表中的 \(K\) 个视觉单词进行匹配,利用内积计算相似度, 内积值越高,表示 \(r_i \)与该视觉单词的相似度越高。通过Softmax归一化,最终得到的 \(v_i \)是 \(r_i \)与所有视觉单词的归一化相似度分布, 即
通过将视觉token \(r_i\) 表示为一个概率分布 \(v_i\) ,实现视觉特征与离散视觉词汇之间的对齐。
视觉嵌入向量
进一步,每个视觉单词在嵌入表中对应一个嵌入向量 \( e_k \in \mathbb{R}^{d'} \),其中 \(d'\) 是嵌入向量的维度。
为了使视觉token和文本token的嵌入具有兼容的形状,设置视觉嵌入表的维度与文本嵌入表的维度相同。
具体的,给定视觉token \(v_i \in \Delta^K\) (一个概率分布),其嵌入向量 \(V_i\) 通过视觉嵌入表计算为:
其中,\(v_{i,k}\) 是 \(v_i\) 的第 \(k \) 个分量,表示视觉token对第 \( k\) 个视觉单词的相关性权重。公式也可以等价地表示为:
这表明 \(V_i\) 是视觉单词嵌入 \(e_k\) 的加权期望值,其中权重由概率分布 \( v_i\) 决定。
- 多义性处理
考虑到视觉patch可能具有多义性,仅将其与一个视觉单词(通过 \(\text{argmax} \, v_{i,j}\) 找到的单词)关联可能会忽略丰富的语义信息。
为了解决这个问题,Ovis方法将视觉patch与多个视觉单词同时关联,这些单词由 \(v_i\) 的非零元素指示。这些元素表示视觉patch与 \(K\) 个视觉单词的相关性。
- 加权组合
最终的视觉patch嵌入 \(V_i\) 是多个视觉单词嵌入的加权组合,权重由 \(v_i\) 的值决定。
这种加权平均方式能够捕获视觉patch的丰富语义,同时保持与文本token嵌入过程的相似性。
训练流程和数据
- Stage 1:视觉编码器微调与视觉-文本对齐
visual_tokenizer.backbone.layer.-1|visual_tokenizer.head|vte
- 重新初始化:视觉编码器 \(g\)的最后一个块的参数
- 训练参数:
- 重新初始化的视觉编码器参数
- 投影矩阵 \(W\)
- 视觉嵌入表 \(\{e_k\}^K_{k=1}\)
- 训练数据 visual captions: COYO-10M
- 实际训练脚本训练使用的数据:
pixelprose-14m|wikipedia-348k|ocr-469k
- 实际训练脚本训练使用的数据:
- 训练样本格式:输入为"<image>'s caption: ",标签为图像的实际描述文本
- Stage2:视觉理解能力增强
visual_tokenizer|vte
- 训练参数:
- 投影矩阵 \(W\)
- 视觉嵌入表 \(\{e_k\}^K_{k=1}\)
- 视觉编码器 $g$ 的所有参数
- 训练数据 visual description: ShareGPT4V-Pretrain等由描述图像的对话的训练样本组成
- 实际训练脚本训练使用的数据:
allava-caption-laion-4v-469k|allava-caption-vflan-4v-195k|cc12m-description-387k
- 实际训练脚本训练使用的数据:
- 训练参数:
- Stage3:多模态指令学习
- 训练参数:模型的所有参数
- 训练目标:使 Ovis 具备遵循多模态指令的能力
- 训练数据:LLaVA-Finetune 等多模态指令数据集
这种渐进式训练策略先让模型学习基本的视觉-文本对齐能力,然后增强其视觉理解能力,最后教会它遵循多模态指令,从而构建一个全面的多模态 AI 系统 下面是文章给出的训练数据表
可以看出这里跟其他模型不同的点是 这里第一个阶段用了大量数据来训练这个视觉嵌入表
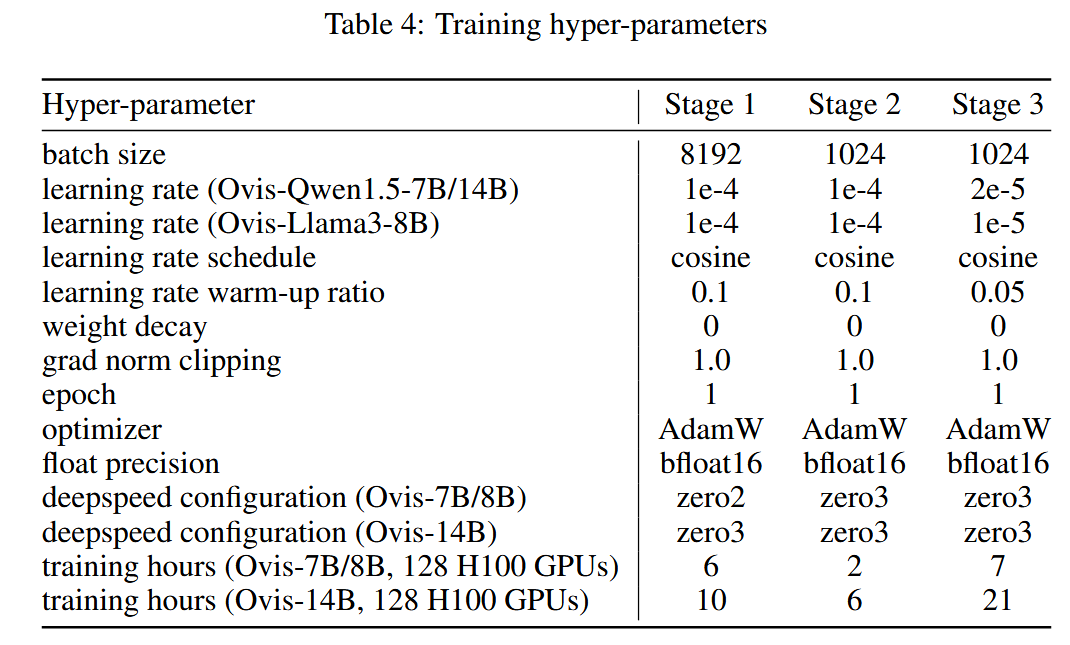
整体模型训练的参数如下:
Ross
https://haochen-wang409.github.io/ross/
ROSS (Reconstructive Visual Instruction Tuning) 是一种新型的大规模多模态模型训练方法。它的核心思想是通过重建输入图像的方式来提供视觉监督信号,从而增强模型的视觉理解能力。
传统多模态模型的条件因果分布可表示为:
其中:
- \(x_i\) 表示第 \(i\) 个 text token
- \(\Theta = \{\theta, \xi, \phi\}\) 表示模型参数
- \(v \in R^{N×D}\) 表示投影后的视觉token
- \(N\)是视觉token数量
- \(D\)是特征通道数
传统的视觉指令调整方法仅监督文本输出,对应的训练目标为:
Ross整体的模型结构如下图所示
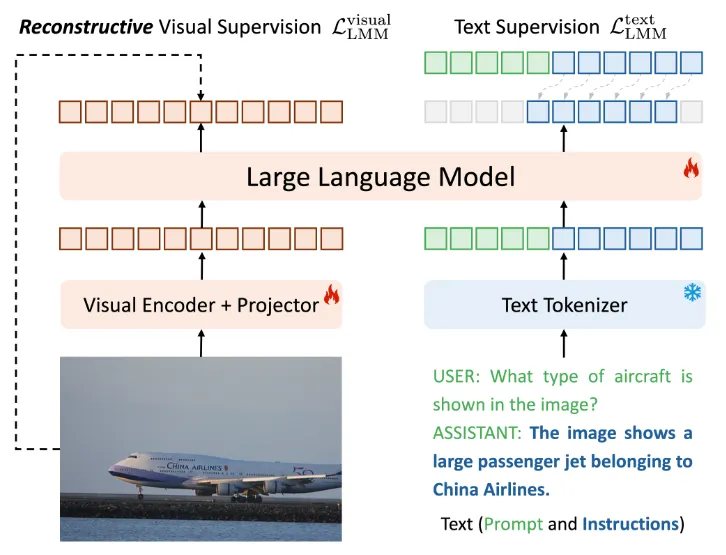
Ross的总体理念是在视觉输出 \(x_{i≤N}\) 上构建重建性视觉监督信号。训练目标包括
- 上图右侧所示的 \(x_{i>N}\) 的原始下一步预测
- 上图左侧的另一个重建项,即 \(L_{Ross} = L_{LMM}^{text} +L_{LMM}^{visual}\)。
具体而言,对于视觉部分可以是 \(x_{i\leq N}\) 和图像 \(I\) 的特定重建目标之间的任何自定义测量值:
具体而言,对于视觉部分可以是 \(x_{i\leq N}\) 和图像 \(I\) 的特定重建目标之间的任何自定义测量值:
其中:
- \(\mathcal{J}_\pi\) 是投影层,将视觉token映射到教师 tokenizer 空间
- \(F\)是教师 tokenizer
- \(M\)是度量函数
针对 \(\mathcal{F}\) 和 \(\mathcal{M}\), 文章尝试和总结了一些方法,我们一步一步来看。
- \(\text{ROSS}^R\) (回归式重建视觉指令)
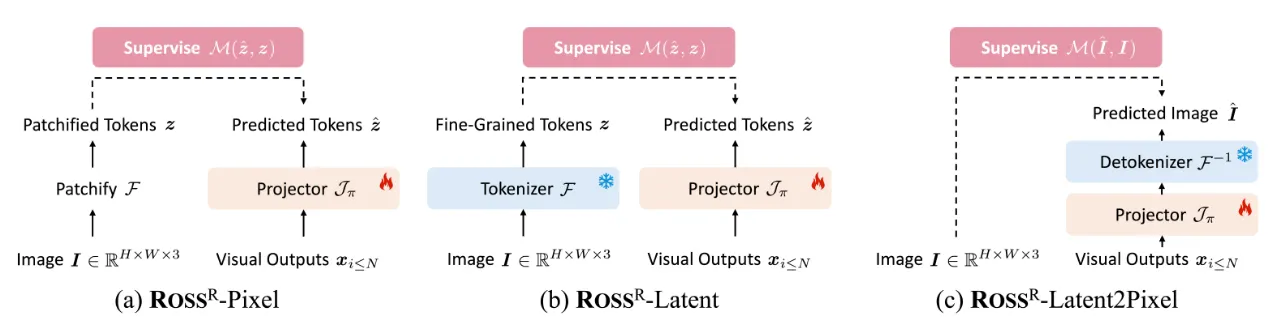
\(\text{ROSS}^R\) (Regressing as Reconstructive Visual Instruction) 提供了三种变体:
- 直接像素回归 \(\text{ROSS}^R\)-Pixel:
- 如上图 (a),\(\mathcal{F}\)为patchify operation(比如ViT)将 图像 \(I \in H\times W \times 3\)转换为一系列2D的patch \(I_p \in R^{N×(3P^2)}\),其中, \(P\)是每个图像patch的分辨率,\(N = HW/P²\)是patch数量
- \(\mathcal{J}_\pi\)可以选择简单的MLP,将视觉输出维度从 \(D\)映射到 \(3P^2\)
- \(\mathcal{M}\)使用MSE作为度量函数
- 视觉信号存在严重的空间冗余,直接回归原始RGB值可能不是为LMM提供有效监督的最佳方式,相比之下,重建潜在表示会是一个更好的选择。
- 回归潜在表示 \(\text{ROSS}^R\)-Latent
- 如上图 (b),\(\mathcal{F}\)可以是判别任务训练的模型(如DINOv2、DEIT-III)或重建任务训练的模型(如VQGAN、VAE)的编码器部分.
- \(\mathcal{M}\)是余弦相似度
- 回归 latent token
- 通过解码回归RGB值 \(\text{ROSS}^R\)-Latent2Pixel
- 使用解码器将预测的潜在表示 \(\hat{z}\)投影到RGB像素空间
- \(\mathcal{F}^{-1}\)是VQGAN或VAE的解码器部分
- \(\mathcal{M}\)是像素空间上的MSE损失
- 直接像素回归 \(\text{ROSS}^R\)-Pixel:
- \(\text{ROSS}^D\)(去噪式重建视觉指令)
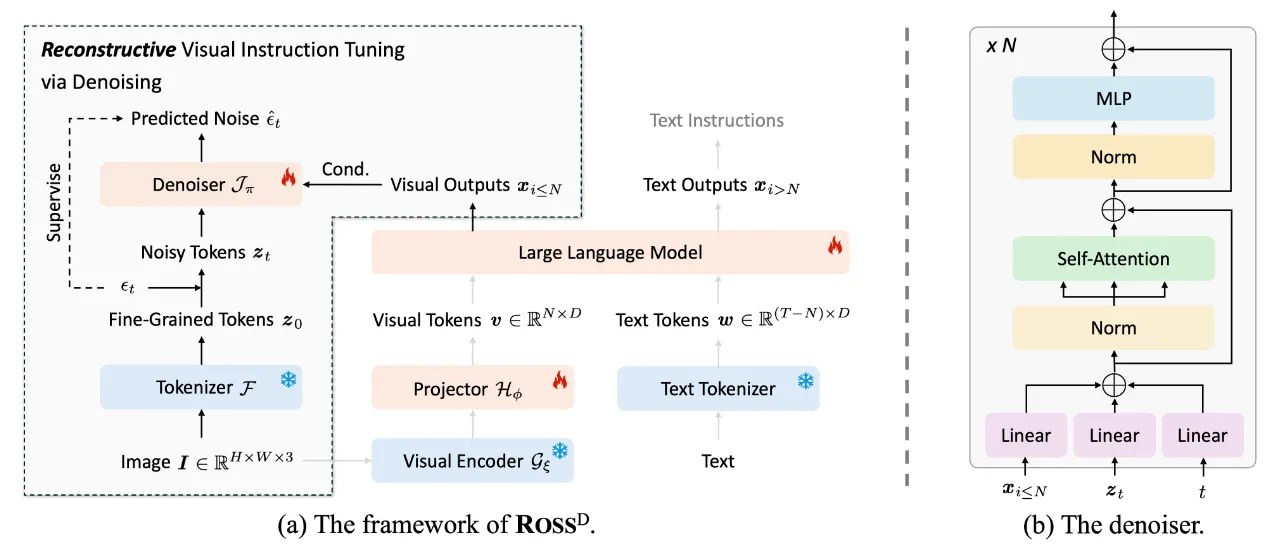
如上图所示,\(\text{ROSS}^D\) 采用扩散模型的去噪目标,以高级视觉输出 \(x_{i\leq N}\) 作为条件,从噪声潜在表示 \(z_t\) 恢复干净的细粒度表示 \(z_0\)。
训练过程遵循扩散过程:
去噪器 \(\mathcal{J}_\pi\) 实际上是估计条件期望 \(E[\epsilon \sim N(0, I)|z_t]\)。
具体的结构为 Transformer编码器块的堆叠,每个块包含三个额外的投影层,用于条件 \(x_{i\leq N}\)、输入噪声 \(z_t\) 和时间步 \(t\)。
默认采用 stable diffusion 中的带KL正则化的连续VAE作为 \(\mathcal{F}\)(代码中使用了Flux.1 中的VAE),因为它能够以低rFID重建输入图像,预期保留输入图像的许多低级细节。
具体模型评估
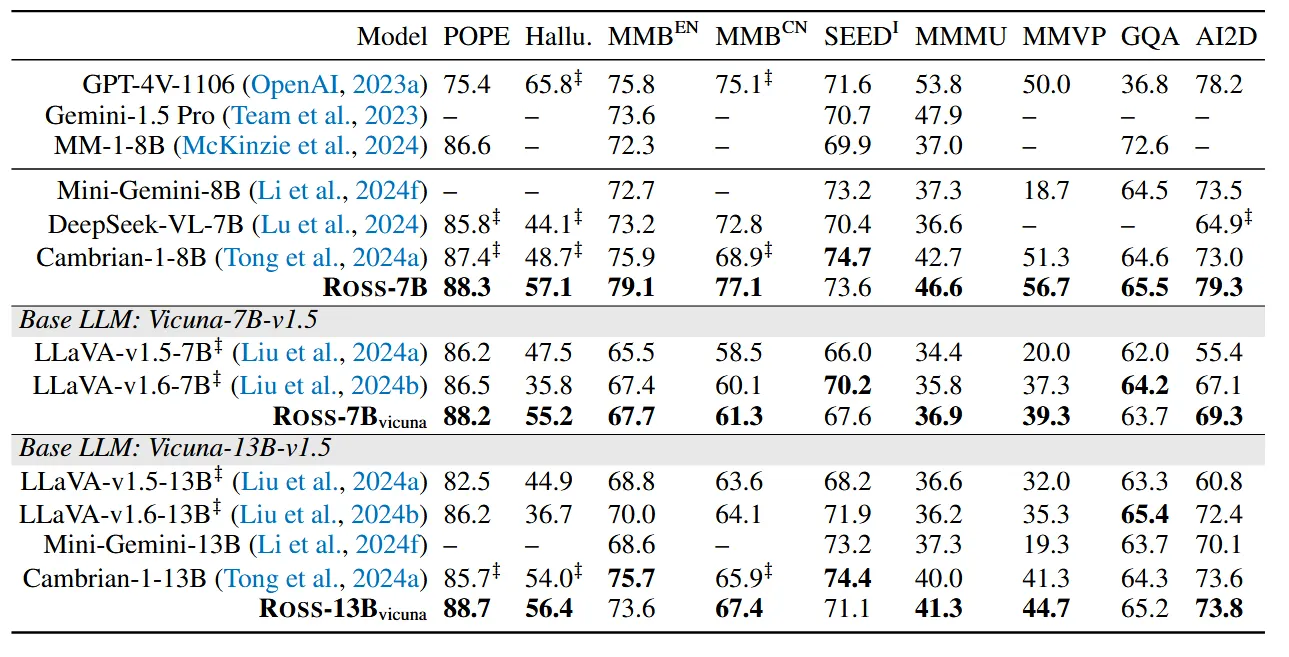
具体的训练参数
GLaMM
这篇论文主要建立图像中各个object和词之间的联系关系,主要贡献在于如何构建这种带关系数据的pipeline。
可以参考:GLaMM
DeepSeek VL
这里简单介绍下 deepseek-vl2
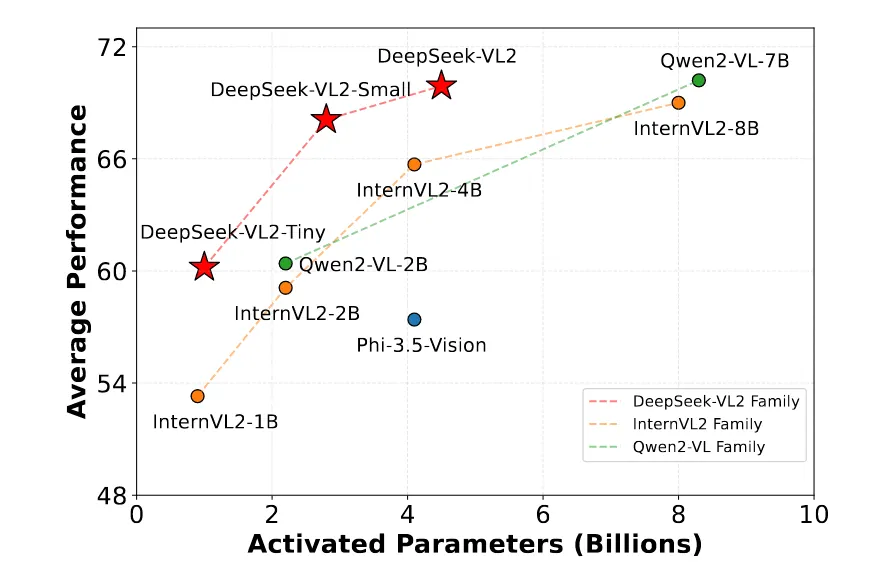
具体的模型结构如下图所示:

基于Llava的结构,增加了一些改进:
- 增加多分辨率
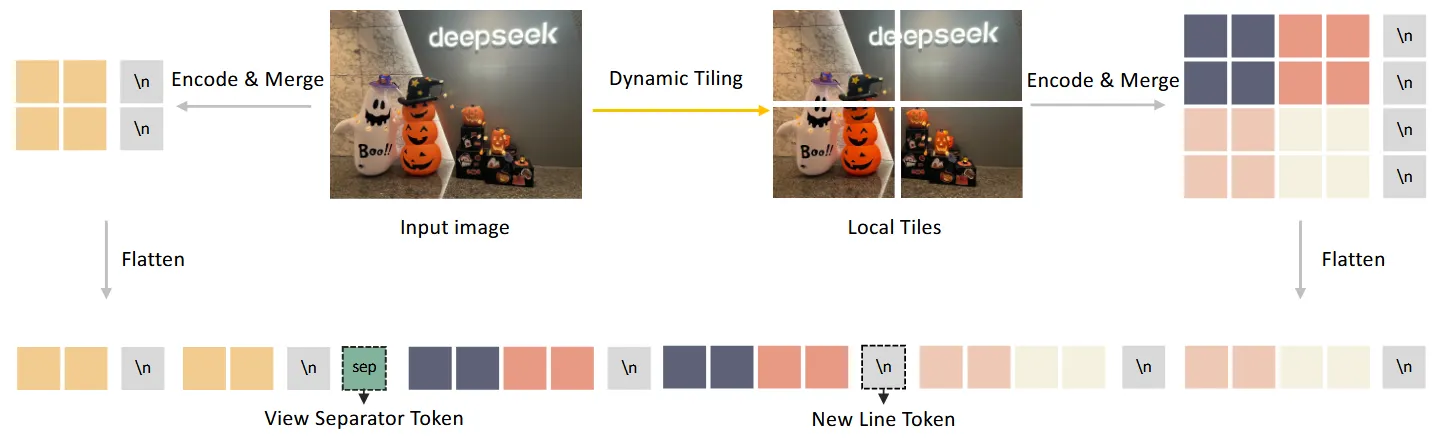
处理流程整体也和llava-onevision中的流程相似:
- 仅使用siglip作为视觉encoder
- 定义一个候选分辨率集合:\(C_R = \{(m · 384, n · 384) | m ∈ N, n ∈ N, 1 ≤ m, n, mn ≤ 9\}\), \(m,n\)是对应的纵横比
- 选择目标分辨率:选择 \((m_i\cdot 384,n_i\cdot 384 )\)作为目标分辨率,使得 padding的区域最小
- Resize: 首先调整原始图像的大小,直到其长边与目标分辨率匹配,然后在保持原始纵横比的同时padding另一个维度。
- 加上原始图像的缩略图,一共可以得到 \((m_i\cdot n_i+1)\)个小图,将每个小图扔进SigLIP中得到对应的embedding(每个小图对应得到1152维度的特征)
- Vision-Language Adaptor: 这里主要增加了一些特殊的token来区分上面的划分,在上图中也有体现:
- 首先会通过一个 \(2\times 2\)的 pixel shuffle操作将token数由 \(27\times 27\)变为 \(14\times 14\)
- 在tiles的每行的末尾都会增加一个
<tile_newline> - 在local和glob图之间会额外增加一个
<view_separator> - 最终的token数量为:\(14\times 15 + 1 + m_i\cdot 14\times(n_i\cdot 14 +1)\)
- 模型结构为一个两层的MLP
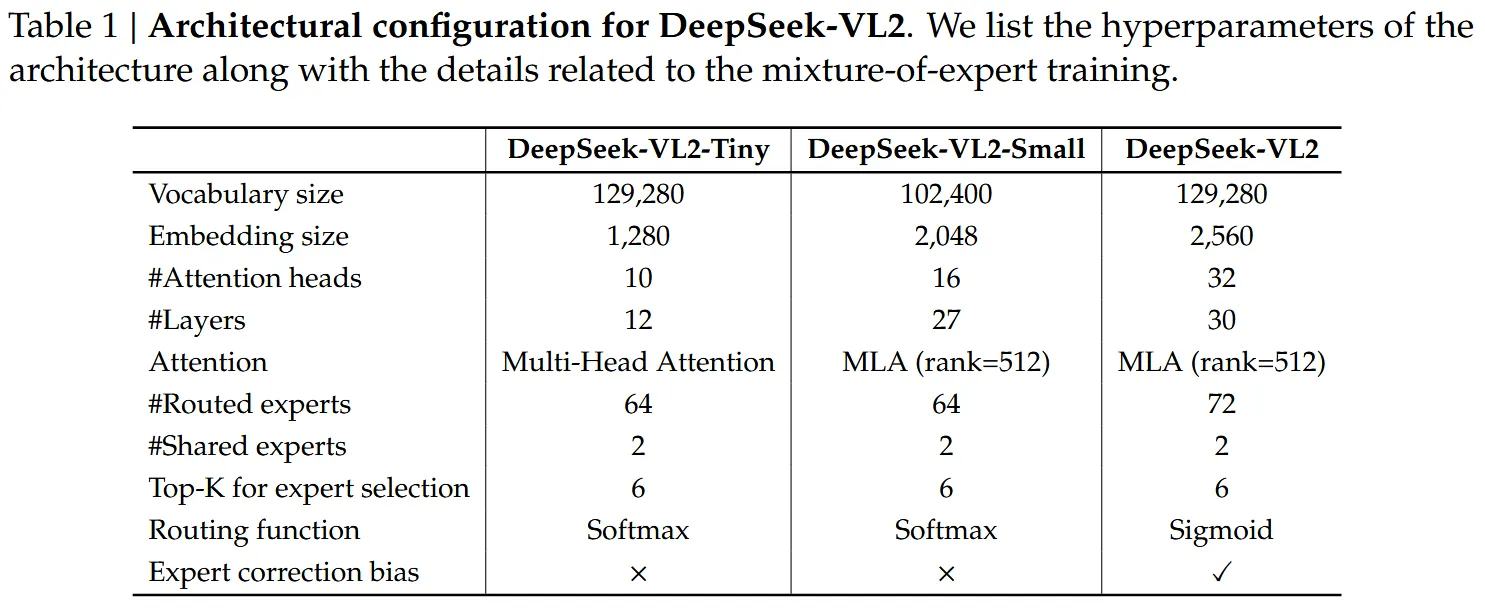
- 带有MLA的DeepSeek MoE结构作为语言模型,结构如下表
MiMo-VL
https://github.com/XiaomiMiMo/MiMo-VL
整体的结构和LLaVA比较像,使用Qwen2.5的视觉encoder,语言模型选择了MiMo-7B-Base
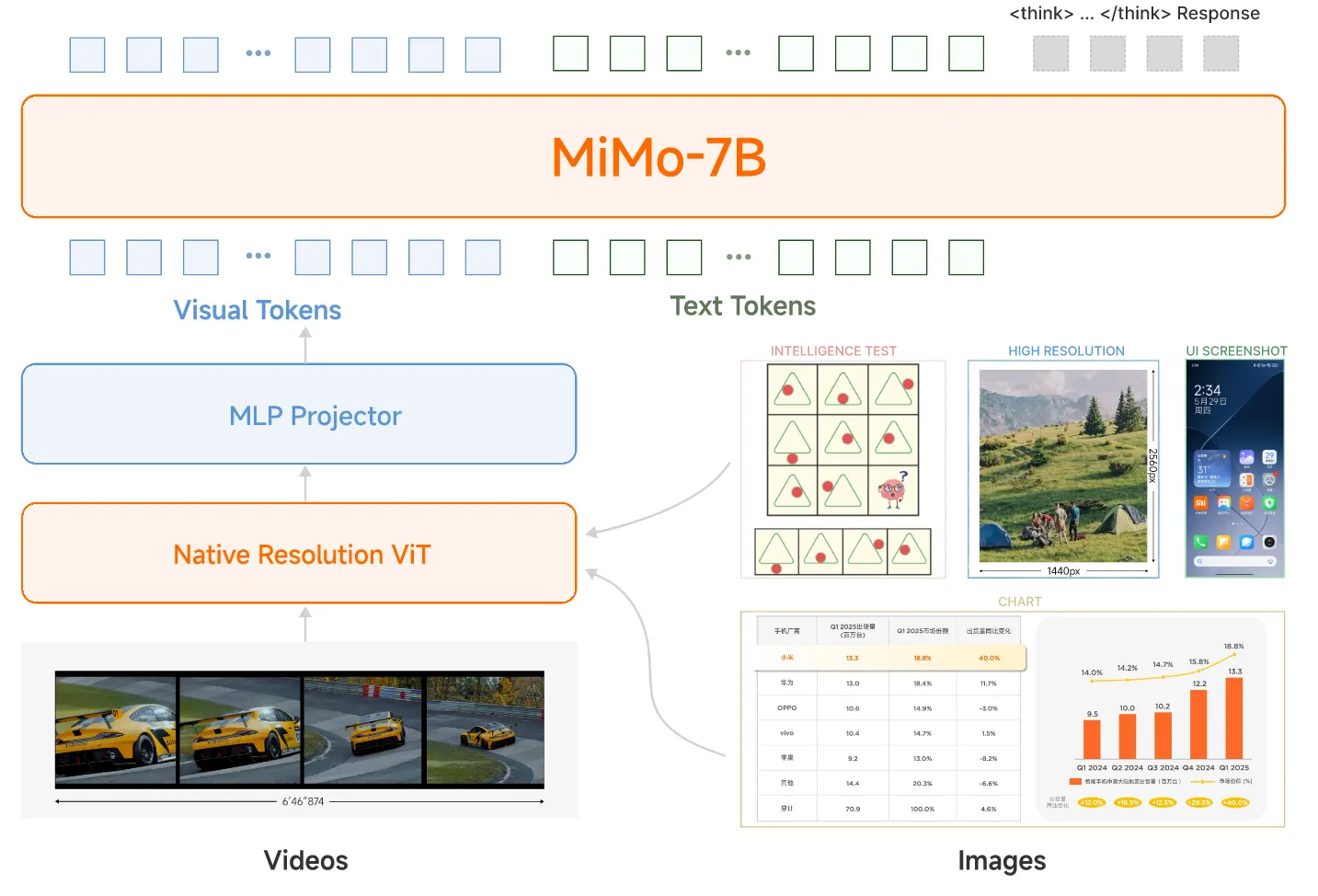
整体比较简单,除了数据上的改变外,整合了一套混合式on-policy 的强化学习(MORL)框架,该框架将强化学习与在RLHF中的可验证奖励强化模型 Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards(RLVR)无缝整合。这里就不赘述了,详情参见:MiMo-VL