训练数据
Pretrain
- 558K Llava pretrain image-text pair
- 695K ALLaVA dataset
Fine-Tuning
Pretrain and Finetune 代码
参数
parser = transformers.HfArgumentParser(
(ModelArguments, DataArguments, TrainingArguments))
首先使用transformers.HfArgumentParser类解析命令行参数,该类的作用是将命令行参数解析为dataclass对象。dataclass是Python3.7中引入的一个新特性,通过dataclass可以方便地定义一个类,并且可以自动实现__init__、__repr__等方法
model_args, data_args, training_args = parser.parse_args_into_dataclasses()
然后通过parser.parse_args_into_dataclasses()方法解析命令行参数,并将解析结果保存到model_args、data_args和training_args三个变量中。
training_args
training args: TrainingArguments(
_n_gpu=1,
accelerator_config={
'split_batches': False,
'dispatch_batches': None,
'even_batches': True,
'use_seedable_sampler': True,
'non_blocking': False,
'gradient_accumulation_kwargs': None,
'use_configured_state': False},
adafactor=False,
adam_beta1=0.9,
adam_beta2=0.999,
adam_epsilon=1e-08,
auto_find_batch_size=False,
batch_eval_metrics=False,
bf16=True,
bf16_full_eval=False,
bits=16,
cache_dir=None,
data_seed=None,
dataloader_drop_last=False,
dataloader_num_workers=4,
dataloader_persistent_workers=False,
dataloader_pin_memory=True,
dataloader_prefetch_factor=None,
ddp_backend=None,
ddp_broadcast_buffers=None,
ddp_bucket_cap_mb=None,
ddp_find_unused_parameters=None,
ddp_timeout=1800,
debug=[],
deepspeed=./scripts/zero2.json,
disable_tqdm=False,
dispatch_batches=None,
do_eval=False,
do_predict=False,
do_train=False,
double_quant=True,
eval_accumulation_steps=None,
eval_delay=0,
eval_do_concat_batches=True,
eval_on_start=False,
eval_steps=None,
eval_strategy=no,
evaluation_strategy=no,
fp16=False,
fp16_backend=auto,
fp16_full_eval=False,
fp16_opt_level=O1,
freeze_mm_mlp_adapter=False,
fsdp=[],
fsdp_config={'min_num_params': 0, 'xla': False, 'xla_fsdp_v2': False, 'xla_fsdp_grad_ckpt': False},
fsdp_min_num_params=0,
fsdp_transformer_layer_cls_to_wrap=None,
full_determinism=False,
gradient_accumulation_steps=2,
gradient_checkpointing=True,
gradient_checkpointing_kwargs=None,
greater_is_better=None,
group_by_length=False,
group_by_modality_length=True,
half_precision_backend=auto,
hub_always_push=False,
hub_model_id=None,
hub_private_repo=False,
hub_strategy=every_save,
hub_token=<HUB_TOKEN>,
ignore_data_skip=False,
include_inputs_for_metrics=False,
include_num_input_tokens_seen=False,
include_tokens_per_second=False,
jit_mode_eval=False,
label_names=None,
label_smoothing_factor=0.0,
learning_rate=2e-05,
length_column_name=length,
load_best_model_at_end=False,
local_rank=0,
log_level=passive,
log_level_replica=warning,
log_on_each_node=True,
logging_dir=/root/autodl-tmp/work_dirs/MGM-7B-HD/runs/Jul23_13-52-28_autodl-container-e94b4883e6-30f10e71,
logging_first_step=False,
logging_nan_inf_filter=True,
logging_steps=1.0,
logging_strategy=steps,
lora_alpha=16,
lora_bias=none,
lora_dropout=0.05,
lora_enable=False,
lora_r=64,
lora_weight_path=,
lr_multi=None,
lr_scheduler_kwargs={},
lr_scheduler_type=cosine,
max_grad_norm=1.0,
max_steps=-1,
metric_for_best_model=None,
mm_projector_lr=None,
model_max_length=4096,
mp_parameters=,
mpt_attn_impl=triton,
neftune_noise_alpha=None,
no_cuda=False,
num_train_epochs=1.0,
optim=adamw_torch,
optim_args=None,
optim_target_modules=None,
output_dir=/root/autodl-tmp/work_dirs/MGM-7B-HD,
overwrite_output_dir=False,
past_index=-1,
per_device_eval_batch_size=4,
per_device_train_batch_size=4,
prediction_loss_only=False,
push_to_hub=False,
push_to_hub_model_id=None,
push_to_hub_organization=None,
push_to_hub_token=<PUSH_TO_HUB_TOKEN>,
quant_type=nf4,
ray_scope=last,
remove_unused_columns=False,
report_to=['wandb'],
restore_callback_states_from_checkpoint=False,
resume_from_checkpoint=None,
run_name=/root/autodl-tmp/work_dirs/MGM-7B-HD,
save_on_each_node=False,
save_only_model=False,
save_safetensors=True,
save_steps=1000,
save_strategy=steps,
save_total_limit=1,
seed=42,
skip_memory_metrics=True,
split_batches=None,
tf32=True,
torch_compile=False,
torch_compile_backend=None,
torch_compile_mode=None,
torchdynamo=None,
tpu_metrics_debug=False,
tpu_num_cores=None,
use_cpu=False,
use_ipex=False,
use_legacy_prediction_loop=False,
use_mps_device=False,
warmup_ratio=0.03,
warmup_steps=0,
weight_decay=0.0,
)
model_args
model args: ModelArguments(
model_name_or_path='/root/autodl-tmp/model_zoo/LLM/vicuna/7B-V1.5',
version='v1',
freeze_backbone=False,
tune_mm_mlp_adapter=False,
vision_tower='/root/autodl-tmp/model_zoo/OpenAI/clip-vit-large-patch14-336',
vision_tower_aux='/root/autodl-tmp/model_zoo/OpenAI/openclip-convnext-large-d-320-laion2B-s29B-b131K-ft-soup',
optimize_vision_tower=False,
optimize_vision_tower_aux=False,
drop_path=True,
image_processor=None,
mm_vision_select_layer=-2,
pretrain_mm_mlp_adapter=None,
mm_projector_type='mlp2x_gelu',
mm_use_im_start_end=False,
mm_use_im_patch_token=False,
mm_vision_select_feature='patch')
data_args
data args: DataArguments(
data_path='/root/autodl-tmp/data/MGM-Finetune/mgm_instruction.json',
lazy_preprocess=True,
is_multimodal=True,
image_folder='/root/autodl-tmp/data/MGM-Finetune',
image_aspect_ratio='pad',
image_grid_pinpoints=None,
image_size_aux=1536,
image_grid=2,
image_global=True)
模型训练前准备
配置训练精度
bnb_model_from_pretrained_args = {}
# default=16 如果使用4位或8位的量化,涉及到QLoRA,需要设置相应的参数
if training_args.bits in [4, 8]:
from transformers import BitsAndBytesConfig
bnb_model_from_pretrained_args.update(dict(
device_map={"": training_args.device},
load_in_4bit=training_args.bits == 4, # 是否加载4位量化模型
load_in_8bit=training_args.bits == 8, # 是否加载8位量化模型
quantization_config=BitsAndBytesConfig(
load_in_4bit=training_args.bits == 4,
load_in_8bit=training_args.bits == 8,
llm_int8_skip_modules=["mm_projector"], # 模块`mm_projector`不进行量化
# 量化阈值设置。
# 如果一个模型的权重或激活值在绝对值上小于 llm_int8_threshold,那么这些值将被量化为8位整形以减少内存使用。
# 如果值的绝对值大于 llm_int8_threshold 则会继续一浮点数的形式存储,保留更多的精度。
llm_int8_threshold=6.0,
# llm_int8_has_fp16_weight用于设置LLM.int8()是否使用16位主权重。
# 该参数控制权重是否在反向传播时进行转换。
llm_int8_has_fp16_weight=False,
# bnb_4bit_compute_dtype设置量化模型的计算数据类型
bnb_4bit_compute_dtype=compute_dtype,
# bnb_4bit_use_double_quant设置是否使用嵌套量化。
# 这将会在第一轮量化之后启用第二轮量化,以便每个参数额外节省 0.4 比特。
bnb_4bit_use_double_quant=training_args.double_quant,
# bnb_4bit_quant_type设置量化数据类型。可以是'fp4'或'nf4'。
bnb_4bit_quant_type=training_args.quant_type # {'fp4', 'nf4'}
)
))
模型权重加载
之后是对模型权重的加载。既然是微调,那就是在已有模型基础上使用数据对模型进行小学习速度的训练。分别对应不同大小的模型,这里提供了Mistral, Mixtral, Gemma 和 Vicuna
if model_args.vision_tower is not None:
if "mistral" in model_args.model_name_or_path.lower():
model = MGMMistralForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
model_args.model_name_or_path,
cache_dir=training_args.cache_dir,
attn_implementation=attn_implementation,
torch_dtype=(torch.bfloat16 if training_args.bf16 else None),
**bnb_model_from_pretrained_args
)
elif "mixtral" in model_args.model_name_or_path.lower():
model = MGMMixtralForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
model_args.model_name_or_path,
cache_dir=training_args.cache_dir,
attn_implementation=attn_implementation,
torch_dtype=(torch.bfloat16 if training_args.bf16 else None),
**bnb_model_from_pretrained_args
)
from deepspeed.utils import set_z3_leaf_modules
set_z3_leaf_modules(model, [MixtralSparseMoeBlock])
elif "gemma" in model_args.model_name_or_path.lower():
model = MGMGemmaForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
model_args.model_name_or_path,
cache_dir=training_args.cache_dir,
attn_implementation=attn_implementation,
torch_dtype=(torch.bfloat16 if training_args.bf16 else None),
**bnb_model_from_pretrained_args
)
else:
model = MGMLlamaForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
model_args.model_name_or_path,
cache_dir=training_args.cache_dir,
attn_implementation=attn_implementation,
torch_dtype=(torch.bfloat16 if training_args.bf16 else None),
**bnb_model_from_pretrained_args
)
else:
model = transformers.LlamaForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
model_args.model_name_or_path,
cache_dir=training_args.cache_dir,
attn_implementation=attn_implementation,
torch_dtype=(torch.bfloat16 if training_args.bf16 else None),
**bnb_model_from_pretrained_args
)
model.config.use_cache = False
if model_args.freeze_backbone:
model.model.requires_grad_(False)
以Vicuna-7B为例:model实例化为MGMLlamaForCausalLM类
LoRA 与梯度设置
通过 peft 库的prepare_model_for_kbit_training 方法让量化模型变成可lora训练
低比特训练(k-bit training)是一种降低模型计算精度的方法,通过将参数表示为低精度浮点数(如 4 位或 8 位)来减少模型计算的复杂度和内存使用。这种方法在大规模模型训练中尤其有用,因为它可以显著减少资源消耗,同时保持模型的性能。
if training_args.bits in [4, 8]:
from peft import prepare_model_for_kbit_training
model.config.torch_dtype = (
torch.float32 if training_args.fp16 else (torch.bfloat16 if training_args.bf16 else torch.float32))
model = prepare_model_for_kbit_training(model, use_gradient_checkpointing=training_args.gradient_checkpointing)
设置保留需要的梯度, 这里主要是输入embeding的梯度:
if training_args.gradient_checkpointing:
if hasattr(model, "enable_input_require_grads"):
model.enable_input_require_grads()
else:
def make_inputs_require_grad(module, input, output):
output.requires_grad_(True)
model.get_input_embeddings().register_forward_hook(make_inputs_require_grad)
梯度检查点(Gradient Checkpointing)是一种节省显存的方法,通常,在反向传播期间,模型的中间激活值需要被保留以计算梯度。启用梯度检查点后,系统只需在需要时计算和保留一部分中间激活值,从而减少内存需求。这对于处理大型模型或限制内存的环境中的训练任务非常有用
之后就根据设置的LoRA参数对模型进行改造了。主要是调用了peft库的get_peft_model函数
if training_args.lora_enable:
from peft import LoraConfig, get_peft_model
lora_config = LoraConfig(
r=training_args.lora_r,
lora_alpha=training_args.lora_alpha,
target_modules=find_all_linear_names(model),
lora_dropout=training_args.lora_dropout,
bias=training_args.lora_bias,
task_type="CAUSAL_LM",
)
if training_args.bits == 16:
if training_args.bf16:
model.to(torch.bfloat16)
if training_args.fp16:
model.to(torch.float16)
rank0_print("Adding LoRA adapters...")
model = get_peft_model(model, lora_config)
这里用到了个函数find_all_linear_names,该函数主要是找出模型中所有的线性层,便于将单个线性层替换为两个LoRA线性层。该函数寻找线性层时跳过了['mm_projector', 'vision_tower', 'vision_resampler', 'vlm_uni'],还跳过了lm_head
def find_all_linear_names(model):
cls = torch.nn.Linear
lora_module_names = set()
multimodal_keywords = ['mm_projector', 'vision_tower', 'vision_resampler', 'vlm_uni']
for name, module in model.named_modules():
if any(mm_keyword in name for mm_keyword in multimodal_keywords):
continue
if isinstance(module, cls):
names = name.split('.')
lora_module_names.add(names[0] if len(names) == 1 else names[-1])
if 'lm_head' in lora_module_names: # needed for 16-bit
lora_module_names.remove('lm_head')
return list(lora_module_names)
token设置
根据模型版本load 一个tokenizer, 并设置对应的conversation 的模板
if 'mpt' in model_args.model_name_or_path:
tokenizer = transformers.AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(
model_args.model_name_or_path,
cache_dir=training_args.cache_dir,
model_max_length=training_args.model_max_length,
padding_side="right"
)
elif "gemma" in model_args.model_name_or_path:
tokenizer = transformers.AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(
model_args.model_name_or_path,
cache_dir=training_args.cache_dir,
model_max_length=training_args.model_max_length,
padding_side="right",
)
else:
# fix bugs after special token with use_fast=True
tokenizer = transformers.AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(
model_args.model_name_or_path,
cache_dir=training_args.cache_dir,
model_max_length=training_args.model_max_length,
padding_side="right",
use_fast=False,
)
if model_args.version == "v0":
if tokenizer.pad_token is None:
smart_tokenizer_and_embedding_resize(
special_tokens_dict=dict(pad_token="[PAD]"),
tokenizer=tokenizer,
model=model,
)
elif model_args.version == "v0.5":
tokenizer.pad_token = tokenizer.unk_token
elif "gemma" in model_args.version:
if model_args.version in conversation_lib.conv_templates:
conversation_lib.default_conversation = conversation_lib.conv_templates[model_args.version]
else:
conversation_lib.default_conversation = conversation_lib.conv_templates["gemma"]
elif "llama_3" in model_args.version:
# set unknown token and pad token to the first reserved special token
if tokenizer.unk_token is None:
tokenizer.unk_token = "<|reserved_special_token_0|>"
tokenizer.pad_token = tokenizer.unk_token
if model_args.version in conversation_lib.conv_templates:
conversation_lib.default_conversation = conversation_lib.conv_templates[model_args.version]
else:
conversation_lib.default_conversation = conversation_lib.conv_templates["llama_3"]
else:
tokenizer.pad_token = tokenizer.unk_token
if model_args.version in conversation_lib.conv_templates:
conversation_lib.default_conversation = conversation_lib.conv_templates[model_args.version]
else:
conversation_lib.default_conversation = conversation_lib.conv_templates["vicuna_v1"]
例如, 这里vicuna对应的模板为:
conv_vicuna_v1 = Conversation(
system="A chat between a curious user and an artificial intelligence assistant. "
"The assistant gives helpful, detailed, and polite answers to the user's questions.",
roles=("USER", "ASSISTANT"),
version="v1",
messages=(),
offset=0,
sep_style=SeparatorStyle.TWO,
sep=" ",
sep2="</s>",
)
加载Vision tower 权重
这里首先初始话模型, 包含加载两个vision encoder 以及multimodal adapter
这里用的vision encoder分别是CLIPVisionTower, OpenCLIPVisionTower 后面模型结构部分再具体介绍, vision tower对应的img process为VideoFramesProcessor
接下来基本都是模型参数赋值,以及对部分模型梯度的freeze, 注意这里, tune_mm_mlp 只去finetune adapter 在pretrain阶段会使用
最后调用initialize_vision_tokenizer, 这个函数主要是处理多模态任务中的特殊标记,并调整模型嵌入层的参数以适应新的任务要求.
if model_args.vision_tower is not None:
# 初始化vision module, 获取对应pretrain权重
model.get_model().initialize_vision_modules(
model_args=model_args,
fsdp=training_args.fsdp
)
vision_tower = model.get_vision_tower()
vision_tower.to(dtype=torch.bfloat16 if training_args.bf16 else torch.float16, device=training_args.device)
data_args.image_processor = copy.deepcopy(vision_tower.image_processor)
data_args.video_processor = copy.deepcopy(vision_tower.image_processor)
data_args.is_multimodal = True
model.config.image_grid = data_args.image_grid
model.config.image_global = data_args.image_global
model.config.image_aspect_ratio = data_args.image_aspect_ratio
model.config.image_grid_pinpoints = data_args.image_grid_pinpoints
model.config.tokenizer_padding_side = tokenizer.padding_side
model.config.tokenizer_model_max_length = tokenizer.model_max_length
# tune_mm_mlp default=False 只去finetune adapter 在pretrain阶段会使用
model.config.tune_mm_mlp_adapter = training_args.tune_mm_mlp_adapter = model_args.tune_mm_mlp_adapter
if model_args.tune_mm_mlp_adapter:
model.requires_grad_(False)
for p in model.get_model().mm_projector.parameters():
p.requires_grad = True
# 冻结adapter
model.config.freeze_mm_mlp_adapter = training_args.freeze_mm_mlp_adapter
if training_args.freeze_mm_mlp_adapter:
for p in model.get_model().mm_projector.parameters():
p.requires_grad = False
if training_args.bits in [4, 8]:
model.get_model().mm_projector.to(dtype=compute_dtype, device=training_args.device)
if model_args.optimize_vision_tower:
print('Optimize last 1/2 layers in vision tower')
total_num = len(vision_tower.vision_tower.vision_model.encoder.layers)
for _idx in range(total_num // 2, total_num):
vision_tower.vision_tower.vision_model.encoder.layers[_idx].requires_grad_(True)
model.config.mm_use_im_start_end = data_args.mm_use_im_start_end = model_args.mm_use_im_start_end
model.config.mm_projector_lr = training_args.mm_projector_lr
training_args.use_im_start_end = model_args.mm_use_im_start_end
model.config.mm_use_im_patch_token = model_args.mm_use_im_patch_token
model.initialize_vision_tokenizer(model_args, tokenizer=tokenizer)
加载vision_tower_aux 与上面类似
数据处理
数据处理被包含在了一个make_supervised_data_module 的函数中
data_module = make_supervised_data_module(tokenizer=tokenizer,
data_args=data_args)
可以看到这个函数主要就是获取Dataset, 以及data_collator(用于处理batch数据)
def make_supervised_data_module(tokenizer: transformers.PreTrainedTokenizer,
data_args) -> Dict:
"""Make dataset and collator for supervised fine-tuning."""
train_dataset = LazySupervisedDataset(tokenizer=tokenizer,
data_path=data_args.data_path,
data_args=data_args)
data_collator = DataCollatorForSupervisedDataset(tokenizer=tokenizer)
return dict(train_dataset=train_dataset,
eval_dataset=None,
data_collator=data_collator)
接下来主要看这个LazySupervisedDataset 类
def __init__(self, data_path: str,
tokenizer: transformers.PreTrainedTokenizer,
data_args: DataArguments):
super(LazySupervisedDataset, self).__init__()
list_data_dict = json.load(open(data_path, "r"))
rank0_print("Formatting inputs...Skip in lazy mode")
self.tokenizer = tokenizer
self.list_data_dict = list_data_dict
self.data_args = data_args
init中主要是获取整体训练数据的list,每个item的形式为(其中有可能会不包含”image”):
{'id': '000000033471',
'image': 'coco/train2017/000000033471.jpg',
'conversations': [{'from': 'human', 'value': '<image>\nWhat are the colors of the bus in the image?'},
{'from': 'gpt', 'value': 'The bus in the image is white and red.'},
{'from': 'human', 'value': 'What feature can be seen on the back of the bus?'},
{'from': 'gpt', 'value': 'The back of the bus features an advertisement.'},
{'from': 'human', 'value': 'Is the bus driving down the street or pulled off to the side?'},
{'from': 'gpt', 'value': 'The bus is driving down the street, which is crowded with people and other vehicles.'}]}
item image前处理
将image pad为正方形, 大小为max(width, height),并交给processer处理
image = Image.open(os.path.join(image_folder, image_file)).convert('RGB')
if self.data_args.image_aspect_ratio == 'pad':
def expand2square(pil_img, background_color):
width, height = pil_img.size
if width == height:
return pil_img
elif width > height:
result = Image.new(pil_img.mode, (width, width), background_color)
result.paste(pil_img, (0, (width - height) // 2))
return result
else:
result = Image.new(pil_img.mode, (height, height), background_color)
result.paste(pil_img, ((height - width) // 2, 0))
return result
image = expand2square(image, tuple(int(x * 255) for x in processor.image_mean))
image = processor.preprocess(image, return_tensors='pt')['pixel_values'][0]
else:
image = processor.preprocess(image, return_tensors='pt')['pixel_values'][0]
这里的processor为 VideoFramesProcessor, 其主要的处理为resize, center_crop, rescale, norm
class VideoFramesProcessor(CLIPImageProcessor):
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
super().__init__(**kwargs)
def preprocess(self, images, **kwargs):
if not isinstance(images, np.ndarray):
return super().preprocess(images=images, **kwargs)
do_resize = kwargs.get('do_resize', self.do_resize)
size = kwargs.get('size', self.size)
size = get_size_dict(size, param_name="size", default_to_square=False)
do_center_crop = kwargs.get('do_center_crop', self.do_center_crop)
crop_size = kwargs.get('crop_size', self.crop_size)
crop_size = get_size_dict(crop_size, param_name="crop_size", default_to_square=True)
do_rescale = kwargs.get('do_rescale', self.do_rescale)
rescale_factor = kwargs.get('rescale_factor', self.rescale_factor)
do_normalize = kwargs.get('do_normalize', self.do_normalize)
image_mean = kwargs.get('image_mean', self.image_mean)
image_std = kwargs.get('image_std', self.image_std)
return_tensors = kwargs.get('return_tensors', None)
def resize(images, output_size):
images = images.permute((0, 3, 1, 2))
images = F.interpolate(images, size=output_size, mode='bicubic')
images = images.permute((0, 2, 3, 1))
return images
def center_crop(images, crop_size):
crop_width, crop_height = crop_size["width"], crop_size["height"]
img_width, img_height = images.shape[1:3]
x = (img_width - crop_width) // 2
y = (img_height - crop_height) // 2
images = images[:, x:x+crop_width, y:y+crop_height]
return images
def rescale(images, rescale_factor):
images = images * rescale_factor
return images
def normalize(images, mean, std):
mean = torch.tensor(mean)
std = torch.tensor(std)
images = (images - mean) / std
return images
images = torch.from_numpy(images).float()
if do_resize:
output_size = get_resize_output_image_size(images[0], size=size["shortest_edge"], default_to_square=False)
images = resize(images, output_size)
if do_center_crop:
images = center_crop(images, crop_size)
if do_rescale:
images = rescale(images, rescale_factor)
if do_normalize:
images = normalize(images, image_mean, image_std)
images = images.permute((0, 3, 1, 2))
data = {"pixel_values": images}
return BatchFeature(data=data, tensor_type=return_tensors)
item conversation处理
其中conversations交给preprocess 这个函数去处理
sources = copy.deepcopy([e["conversations"] for e in sources])
has_image = ('image' in self.list_data_dict[i])
data_dict = preprocess(
sources,
self.tokenizer,
has_image=has_image)
if isinstance(i, int):
data_dict = dict(input_ids=data_dict["input_ids"][0],
labels=data_dict["labels"][0])
这个函数给了注释:
对于给定的sources,每个source都是一个对话列表。做以下变换:
- 每句开头添加信号'###',结束信号'\n';
- 将对话串联起来;
- tokenize串联后的对话;
- 使用 IGNORE_INDEX 屏蔽人类单词作为label。
def preprocess_v1( sources, tokenizer: transformers.PreTrainedTokenizer, has_image: bool = False ) -> Dict: conv = conversation_lib.default_conversation.copy() roles = {"human": conv.roles[0], "gpt": conv.roles[1]} # Apply prompt templates conversations = [] for i, source in enumerate(sources): if roles[source[0]["from"]] != conv.roles[0]: # Skip the first one if it is not from human source = source[1:] conv.messages = [] for j, sentence in enumerate(source): role = roles[sentence["from"]] assert role == conv.roles[j % 2], f"{i}" conv.append_message(role, sentence["value"]) conversations.append(conv.get_prompt()) # Tokenize conversations if has_image: input_ids = torch.stack( [tokenizer_image_token(prompt, tokenizer, return_tensors='pt') for prompt in conversations], dim=0) else: input_ids = tokenizer( conversations, return_tensors="pt", padding="longest", max_length=tokenizer.model_max_length, truncation=True, ).input_ids targets = input_ids.clone() assert conv.sep_style == conversation_lib.SeparatorStyle.TWO # Mask targets sep = conv.sep + conv.roles[1] + ": " for conversation, target in zip(conversations, targets): total_len = int(target.ne(tokenizer.pad_token_id).sum()) rounds = conversation.split(conv.sep2) cur_len = 1 target[:cur_len] = IGNORE_INDEX for i, rou in enumerate(rounds): if rou == "": break parts = rou.split(sep) if len(parts) != 2: print(f"WARNING: parts!=: {parts}") break parts[0] += sep if has_image: round_len = len(tokenizer_image_token(rou, tokenizer)) instruction_len = len(tokenizer_image_token(parts[0], tokenizer)) - 2 else: round_len = len(tokenizer(rou).input_ids) instruction_len = len(tokenizer(parts[0]).input_ids) - 2 if i != 0 and not getattr(tokenizer, "legacy", False) and IS_TOKENIZER_GREATER_THAN_0_14: round_len -= 1 instruction_len -= 1 target[cur_len: cur_len + instruction_len] = IGNORE_INDEX cur_len += round_len target[cur_len:] = IGNORE_INDEX if cur_len < tokenizer.model_max_length: if cur_len != total_len: target[:] = IGNORE_INDEX print( f"WARNING: tokenization mismatch: {cur_len} vs. {total_len}." f" (ignored)" ) return dict( input_ids=input_ids, labels=targets, )
最终输出的形式如下 :
input_ids
tensor([[ 1, 319, 13563, 1546, 263, 12758, 1404, 322, 385, 23116,
21082, 20255, 29889, 450, 20255, 4076, 8444, 29892, 13173, 29892,
322, 1248, 568, 6089, 304, 278, 1404, 29915, 29879, 5155,
29889, 3148, 1001, 29901, 29871, -200, 29871, 13, 5618, 526,
278, 11955, 310, 278, 3593, 297, 278, 1967, 29973, 319,
1799, 9047, 13566, 29901, 450, 3593, 297, 278, 1967, 338,
4796, 322, 2654, 29889, 2, 11889, 29901, 1724, 4682, 508,
367, 3595, 373, 278, 1250, 310, 278, 3593, 29973, 319,
1799, 9047, 13566, 29901, 450, 1250, 310, 278, 3593, 5680,
385, 18811, 275, 882, 29889, 2, 11889, 29901, 1317, 278,
3593, 19500, 1623, 278, 11952, 470, 20043, 1283, 304, 278,
2625, 29973, 319, 1799, 9047, 13566, 29901, 450, 3593, 338,
19500, 1623, 278, 11952, 29892, 607, 338, 11660, 7176, 411,
2305, 322, 916, 24413, 29889, 2]])
targets
tensor([[ -100, -100, -100, -100, -100, -100, -100, -100, -100, -100,
-100, -100, -100, -100, -100, -100, -100, -100, -100, -100,
-100, -100, -100, -100, -100, -100, -100, -100, -100, -100,
-100, -100, -100, -100, -100, -100, -100, -100, -100, -100,
-100, -100, -100, -100, -100, -100, -100, -100, -100, -100,
-100, -100, -100, -100, 450, 3593, 297, 278, 1967, 338,
4796, 322, 2654, 29889, 2, -100, -100, -100, -100, -100,
-100, -100, -100, -100, -100, -100, -100, -100, -100, -100,
-100, -100, -100, -100, 450, 1250, 310, 278, 3593, 5680,
385, 18811, 275, 882, 29889, 2, -100, -100, -100, -100,
-100, -100, -100, -100, -100, -100, -100, -100, -100, -100,
-100, -100, -100, -100, -100, -100, -100, 450, 3593, 338,
19500, 1623, 278, 11952, 29892, 607, 338, 11660, 7176, 411,
2305, 322, 916, 24413, 29889, 2]])
处理图像(HR flow and LR flow)
其中, image_size_raw: {'height': 336, 'width': 336}, self.data_args.image_grid=2, self.data_args.image_processor.crop_size=1536
- 根据
image_grid对原图像进行双线性插值得到shape为raw_shape大小的图像作为data_dict['image'] - 如果item中不包含图像且
is_multimodal=True, 生成两个全 0 tensor,data_dict['image']和data_dict['image_aux'],image_aux大小为crop_size - 将
data_dict['image']按照grid大小切片和原大小做concat, 对应论文中 visual token extension部分
if hasattr(self.data_args, 'image_size_raw') and (image is not None): data_dict['image_aux'] = image.clone() raw_shape = [self.data_args.image_size_raw['height'] * self.data_args.image_grid, self.data_args.image_size_raw['width'] * self.data_args.image_grid] # only apply when input is image if 'image' in self.list_data_dict[i]: if len(image.shape) == 3: image = torch.nn.functional.interpolate(image[None], size=raw_shape, mode='bilinear', align_corners=False)[0] else: image = torch.nn.functional.interpolate(image, size=raw_shape, mode='bilinear', align_corners=False) # image exist in the data if 'image' in self.list_data_dict[i]: data_dict['image'] = image elif self.data_args.is_multimodal: # image does not exist in the data, but the model is multimodal crop_size = self.data_args.image_processor.crop_size # 1536 if hasattr(self.data_args, 'image_size_raw'): # 336 data_dict['image'] = torch.zeros(3, self.data_args.image_size_raw['height'] * self.data_args.image_grid, self.data_args.image_size_raw['width'] * self.data_args.image_grid) data_dict['image_aux'] = torch.zeros(3, crop_size['height'], crop_size['width']) else: data_dict['image'] = torch.zeros(3, crop_size['height'], crop_size['width']) if 'image' in data_dict and self.data_args.image_grid >= 2: raw_image = data_dict['image'].reshape(3, self.data_args.image_grid, self.data_args.image_size_raw['height'], self.data_args.image_grid, self.data_args.image_size_raw['width']) raw_image = raw_image.permute(1, 3, 0, 2, 4) raw_image = raw_image.reshape(-1, 3, self.data_args.image_size_raw['height'], self.data_args.image_size_raw['width']) if self.data_args.image_global: global_image = data_dict['image'] if len(global_image.shape) == 3: global_image = global_image[None] global_image = torch.nn.functional.interpolate(global_image, size=[self.data_args.image_size_raw['height'], self.data_args.image_size_raw['width']], mode='bilinear', align_corners=False) # [image_crops, image_global] raw_image = torch.cat([raw_image, global_image], dim=0) data_dict['image'] = raw_image.contiguous()
最终data_dict就包含image :LR, image_aux :HR,labels和input_ids, 送入data_collator中组成batch
@dataclass
class DataCollatorForSupervisedDataset(object):
"""Collate examples for supervised fine-tuning."""
tokenizer: transformers.PreTrainedTokenizer
def __call__(self, instances: Sequence[Dict]) -> Dict[str, torch.Tensor]:
input_ids, labels = tuple([instance[key] for instance in instances]
for key in ("input_ids", "labels"))
input_ids = torch.nn.utils.rnn.pad_sequence(
input_ids,
batch_first=True,
padding_value=self.tokenizer.pad_token_id)
labels = torch.nn.utils.rnn.pad_sequence(labels,
batch_first=True,
padding_value=IGNORE_INDEX)
input_ids = input_ids[:, :self.tokenizer.model_max_length]
labels = labels[:, :self.tokenizer.model_max_length]
batch = dict(
input_ids=input_ids,
labels=labels,
attention_mask=input_ids.ne(self.tokenizer.pad_token_id),
)
if 'image' in instances[0]:
images = [instance['image'] for instance in instances]
# not concat for couple images
if all(x is not None and x.shape == images[0].shape and len(x) != 2 for x in images) and len(images) > 1:
batch['images'] = torch.stack(images)
else:
batch['images'] = images
if 'image_aux' in instances[0]:
images = [instance['image_aux'] for instance in instances]
if all(x is not None and x.shape == images[0].shape for x in images) and len(images) > 1:
batch['images_aux'] = torch.stack(images)
else:
batch['images_aux'] = images
return batch
模型训练
将model, data和训练参数传给trainer进行模型训练
trainer = LLaVATrainer(model=model,
tokenizer=tokenizer,
args=training_args,
**data_module)
if list(pathlib.Path(training_args.output_dir).glob("checkpoint-*")):
trainer.train(resume_from_checkpoint=True)
else:
trainer.train()
trainer.save_state()
这里LLaVATrainer 继承Trainer做了几点改变,一是调了自己的*optimizer*, 另外根据数据集的modality_lengths拿到的length list 进行分组采样
@property
def modality_lengths(self):
length_list = []
for sample in self.list_data_dict:
cur_len = sum(len(conv['value'].split()) for conv in sample['conversations'])
cur_len = cur_len if ('image' in sample) else -cur_len
length_list.append(cur_len)
return length_list
模型结构
MGMConfig
MGMConfig {
"_name_or_path": "/root/autodl-tmp/model_zoo/LLM/vicuna/7B-V1.5",
"architectures": [
"LlamaForCausalLM"
],
"attention_bias": false,
"attention_dropout": 0.0,
"bos_token_id": 1,
"eos_token_id": 2,
"freeze_mm_mlp_adapter": false,
"hidden_act": "silu",
"hidden_size": 4096,
"image_aspect_ratio": "pad",
"image_global": true,
"image_grid": 2,
"image_grid_pinpoints": null,
"image_size_aux": 1536,
"initializer_range": 0.02,
"intermediate_size": 11008,
"max_position_embeddings": 4096,
"mlp_bias": false,
"mm_hidden_size": 1024,
"mm_hidden_size_aux": 2880,
"mm_projector_lr": null,
"mm_projector_type": "mlp2x_gelu",
"mm_use_im_patch_token": false,
"mm_use_im_start_end": false,
"mm_vision_select_feature": "patch",
"mm_vision_select_layer": -2,
"mm_vision_tower": "/root/autodl-tmp/model_zoo/OpenAI/clip-vit-large-patch14-336",
"mm_vision_tower_aux": "/root/autodl-tmp/model_zoo/OpenAI/openclip-convnext-large-d-320-laion2B-s29B-b131K-ft-soup",
"model_type": "mgm",
"num_attention_heads": 32,
"num_hidden_layers": 32,
"num_key_value_heads": 32,
"optimize_vision_tower": false,
"optimize_vision_tower_aux": false,
"pad_token_id": 0,
"pretraining_tp": 1,
"rms_norm_eps": 1e-05,
"rope_scaling": null,
"rope_theta": 10000.0,
"tie_word_embeddings": false,
"tokenizer_model_max_length": 4096,
"tokenizer_padding_side": "right",
"torch_dtype": "float16",
"transformers_version": "4.42.3",
"tune_mm_mlp_adapter": false,
"use_cache": false,
"use_mm_proj": true,
"vocab_size": 32000
}
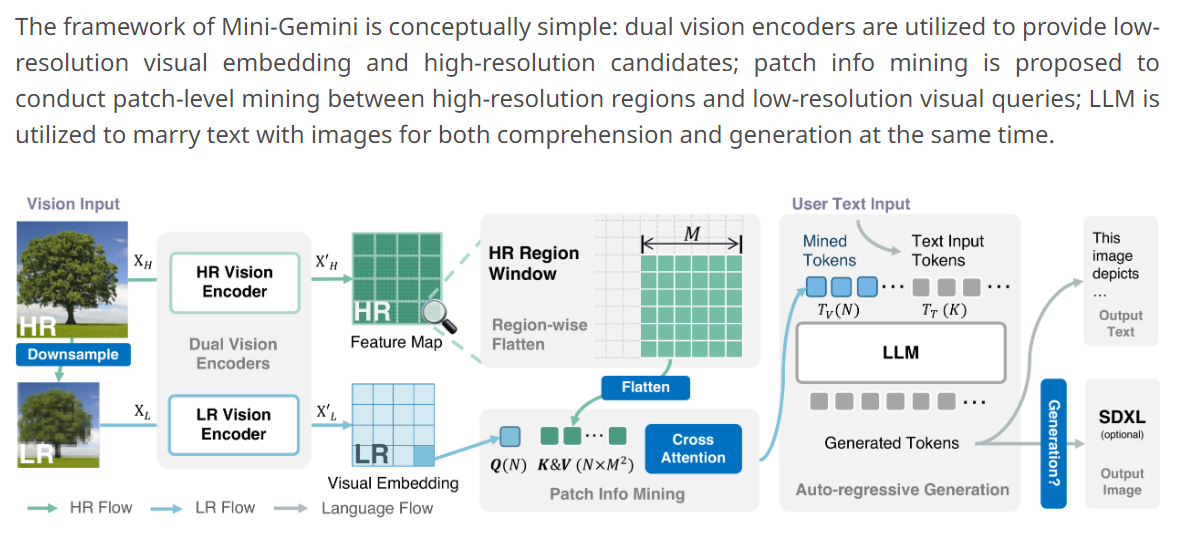
视觉模型和多模态特征融合
处理文本和视觉数据的多模态模型准备输入和标签 对应在MGMLlamaForCausalLM的forward中
if inputs_embeds is None:
(
input_ids,
position_ids,
attention_mask,
past_key_values,
inputs_embeds,
labels
) = self.prepare_inputs_labels_for_multimodal(
input_ids,
position_ids,
attention_mask,
past_key_values,
labels,
images,
images_aux
)
prepare_inputs_labels_for_multimodal做的事情主要是:
- 处理图像输入的边缘情况
- 图像encoding, 这里的流程就是Patch info Mining 的过程, 总的来说就是分成两个pipeline:
- 初始化
**attention_mask****position_ids** - 移除填充并更新输入嵌入和标签