导言
自监督学习(Self-Supervised Learning)能利用大量无标注的数据进行表征学习,然后在特定下游任务上对参数进行微调。通过这样的方式,能够在较少有标注数据上取得优于有监督学习方法的精度。近年来,自监督学习受到了越来越多的关注,如Yann Lecun也在 AAAI 上讲 Self-Supervised Learning 是未来的大势所趋。在CV领域涌现了如SwAV、MOCO、DINO、MoBY等一系列工作。MAE是kaiming继MOCO之后在自监督学习领域的又一力作。首先,本文会对MAE进行解读,然后基于EasyCV库的精度复现过程及其中遇到的一些问题作出解答。
概述
MAE的做法很简单:随机mask掉图片中的一些patch,然后通过模型去重建这些丢失的区域。包括两个核心的设计:1.非对称编码-解码结构 2.用较高的掩码率(75%)。通过这两个设计MAE在预训练过程中可以取得3倍以上的训练速度和更高的精度,如ViT-Huge能够通过ImageNet-1K数据上取得87.8%的准确率。
模型拆解
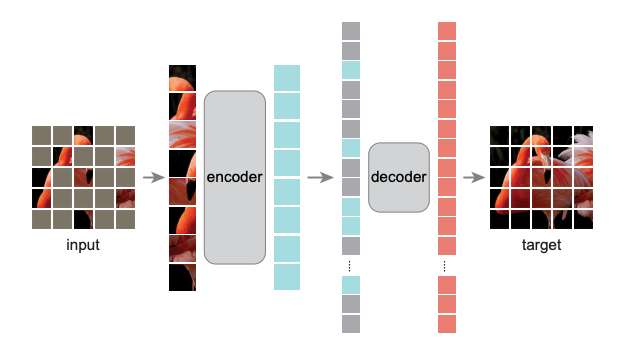
MAE属于自编码器(AutoEncoder)的一种,由编码器和解码器两个部分组成。类似于常见的自编码器,MAE会先通过编码器将图片patch映射到隐空间。然后,基于解码器将隐空间上的特征变量重构成图片patch。和常见自编码器的区别是非对称的编码解码结构。这个非对称性主要体现在以下两点:
- 轻量化的解码器结构
- 在编码器阶段,仅将未被mask掉的图片patch作为输入。在解码器阶段会将编码器输出的隐变量和mask token共同作为输入去重建完成的图片。
掩码策略
首先,直接采用ViT的做法将图片分成不重叠的patch(如vit-b会将图片划分成16x16的图像块),然后通过均匀采样策略对这些patch进行采样,并丢弃未被选中的部分。MAE所采用的掩码策略有如下两个特点:
1.在算法中,使用了75%的masking ratio来丢弃图片patch。作者指出,通过high masking ratio可以有效减少输入的冗余程度,使重建任务不能够通过简单的参考邻近patch来完成。文中,也通过实验证明了这一观点。
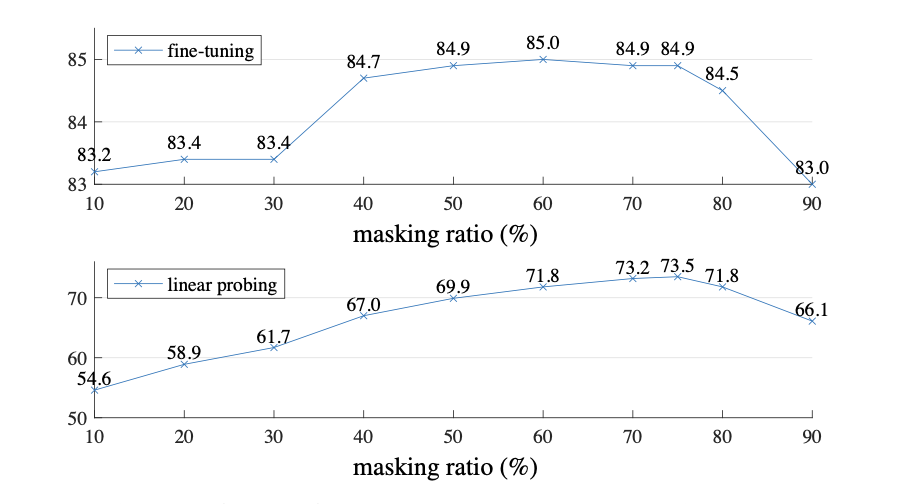
关于Masking ratio的实验是MAE最精彩的一部分,随着mask ratio的增加,fine-tuning和linear proing(指针对最后的线性层做微调)的精度逐渐攀升,甚至到75%还没有下降,这一点打破了BERT(15%)、BEiT(40%)的做法,进一步将mask 预训练方式在NLP领域的成功在CV领域实现复制。
2.采用了均匀采样策略可以有效的避免potential center bias(丢弃掉的patch都靠近图片中心)。对mask策略的消去实验如下表所示。

解码器
MAE decoder由一连串的Transfomer block组成。和encoder不同的是,MAE decoder的输入不仅包括未被mask的图像patch经过encoder编码后的特征,还包括了被mask掉的部分。对于mask掉部分的输入,会用一个共享参数,且可学习的mask token代替作为输入。除此之外,为了保证不同的mask token能够区分在图像中的不同位置,在输入到decoder之前,会对整体的输入加上positional embedding。
在MAE中,解码器仅会在预训练阶段用于图片的重建工作。文中采用了轻量化的解码器结构,对于每个token的计算量仅有相对于解码器的10%以下。通过这种设计,就算在解码阶段用了完整数量的token作为输入,对计算资源的消耗也不会显著增加。
文中,作者对解码器的depth和width两个维度进行对比实验,可以看出一个较轻量化的解码器,就足以是模型学习到有效的表征。
重建目标
MAE预训练任务的目标是重建被mask掉的像素值。MAE decoder输出关于每个图像patch的表征后,会经过一个linear projection层映射成与图像像素数目相同维度的向量(\(P\times P \times 3\))。仅采用MSE作为损失函数,计算预测向量和被mask掉像素值之前的MSE loss。
需要额外指出的是,作者使用了归一化后的图像patch作为重建的目标。通过实验证明,这种做法可以提升模型的表征能力。
模型评价
文中除了从linear probing和Finetuning两个角度对模型的表征能力做出评价外,还采用了Partial Fine-tuning的方式进行评价,相比于linear probing这种之前普遍采用的评价方式,能够更好的反映预训练模型对非线性特征的表征能力。从下图可以看出,MAE算法仅仅对一个transformer block进行fintune精度就从73.5%提升到81%。同时与MOCOv3相比,MOCOv3虽然在linear probing的时候具有更高的精度,但是在partial fine-tuning时,MAE的精度都要高于MOCOv3。可以看出,MAE虽然对线性特征的表征能力要弱于MOCOv3,但是具有更好的非线性特征表征能力。

代码复现
class MaskedAutoencoderViT(nn.Module):
""" Masked Autoencoder with VisionTransformer backbone
"""
def __init__(self, img_size=224, patch_size=16, in_chans=3,
embed_dim=1024, depth=24, num_heads=16,
decoder_embed_dim=512, decoder_depth=8, decoder_num_heads=16,
mlp_ratio=4., norm_layer=nn.LayerNorm, norm_pix_loss=False):
super().__init__()
# --------------------------------------------------------------------------
# MAE encoder specifics
self.patch_embed = PatchEmbed(img_size, patch_size, in_chans, embed_dim)
num_patches = self.patch_embed.num_patches
self.cls_token = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(1, 1, embed_dim))
self.pos_embed = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(1, num_patches + 1, embed_dim),
requires_grad=False) # fixed sin-cos embedding
self.blocks = nn.ModuleList([
Block(embed_dim, num_heads, mlp_ratio, qkv_bias=True, qk_scale=None, norm_layer=norm_layer)
for i in range(depth)])
self.norm = norm_layer(embed_dim)
# --------------------------------------------------------------------------
# --------------------------------------------------------------------------
# MAE decoder specifics
self.decoder_embed = nn.Linear(embed_dim, decoder_embed_dim, bias=True)
self.mask_token = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(1, 1, decoder_embed_dim))
self.decoder_pos_embed = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(1, num_patches + 1, decoder_embed_dim),
requires_grad=False) # fixed sin-cos embedding
self.decoder_blocks = nn.ModuleList([
Block(decoder_embed_dim, decoder_num_heads, mlp_ratio, qkv_bias=True, qk_scale=None, norm_layer=norm_layer)
for i in range(decoder_depth)])
self.decoder_norm = norm_layer(decoder_embed_dim)
self.decoder_pred = nn.Linear(decoder_embed_dim, patch_size ** 2 * in_chans, bias=True) # encoder to decoder
# --------------------------------------------------------------------------
self.norm_pix_loss = norm_pix_loss
self.initialize_weights()
# 将图像 (N, C, H, W) 转换为patch (N, H*W/p^2, p^2*3)
def patchify(self, imgs):
"""
imgs: (N, 3, H, W)
x: (N, L, patch_size**2 *3)
"""
p = self.patch_embed.patch_size[0]
assert imgs.shape[2] == imgs.shape[3] and imgs.shape[2] % p == 0
h = w = imgs.shape[2] // p
x = imgs.reshape(shape=(imgs.shape[0], 3, h, p, w, p))
x = torch.einsum('nchpwq->nhwpqc', x)
x = x.reshape(shape=(imgs.shape[0], h * w, p ** 2 * 3))
return x
def unpatchify(self, x):
"""
x: (N, L, patch_size**2 *3)
imgs: (N, 3, H, W)
"""
p = self.patch_embed.patch_size[0]
h = w = int(x.shape[1] ** .5)
assert h * w == x.shape[1]
x = x.reshape(shape=(x.shape[0], h, w, p, p, 3))
x = torch.einsum('nhwpqc->nchpwq', x)
imgs = x.reshape(shape=(x.shape[0], 3, h * p, h * p))
return imgs
def random_masking(self, x, mask_ratio):
"""
Perform per-sample random masking by per-sample shuffling.
Per-sample shuffling is done by argsort random noise.
x: [N, L, D], sequence
"""
N, L, D = x.shape # batch, length, dim
len_keep = int(L * (1 - mask_ratio))
noise = torch.rand(N, L, device=x.device) # noise in [0, 1]
# sort noise for each sample
ids_shuffle = torch.argsort(noise, dim=1) # ascend: small is keep, large is remove
ids_restore = torch.argsort(ids_shuffle, dim=1)
# keep the first subset
ids_keep = ids_shuffle[:, :len_keep]
x_masked = torch.gather(x, dim=1, index=ids_keep.unsqueeze(-1).repeat(1, 1, D))
# generate the binary mask: 0 is keep, 1 is remove
mask = torch.ones([N, L], device=x.device)
mask[:, :len_keep] = 0
# unshuffle to get the binary mask
mask = torch.gather(mask, dim=1, index=ids_restore)
return x_masked, mask, ids_restore
def forward_encoder(self, x, mask_ratio):
# embed patches
x = self.patch_embed(x)
# add pos embed w/o cls token
x = x + self.pos_embed[:, 1:, :]
# masking: length -> length * mask_ratio
x, mask, ids_restore = self.random_masking(x, mask_ratio)
# append cls token
cls_token = self.cls_token + self.pos_embed[:, :1, :]
cls_tokens = cls_token.expand(x.shape[0], -1, -1)
x = torch.cat((cls_tokens, x), dim=1)
# apply Transformer blocks
for blk in self.blocks:
x = blk(x)
x = self.norm(x)
return x, mask, ids_restore
def forward_decoder(self, x, ids_restore):
# embed tokens
x = self.decoder_embed(x)
# append mask tokens to sequence
mask_tokens = self.mask_token.repeat(x.shape[0], ids_restore.shape[1] + 1 - x.shape[1], 1)
x_ = torch.cat([x[:, 1:, :], mask_tokens], dim=1) # no cls token
x_ = torch.gather(x_, dim=1, index=ids_restore.unsqueeze(-1).repeat(1, 1, x.shape[2])) # unshuffle
x = torch.cat([x[:, :1, :], x_], dim=1) # append cls token
# add pos embed
x = x + self.decoder_pos_embed
# apply Transformer blocks
for blk in self.decoder_blocks:
x = blk(x)
x = self.decoder_norm(x)
# predictor projection
x = self.decoder_pred(x)
# remove cls token
x = x[:, 1:, :]
return x
def forward_loss(self, imgs, pred, mask):
"""
imgs: [N, 3, H, W]
pred: [N, L, p*p*3]
mask: [N, L], 0 is keep, 1 is remove,
"""
target = self.patchify(imgs)
if self.norm_pix_loss:
mean = target.mean(dim=-1, keepdim=True)
var = target.var(dim=-1, keepdim=True)
target = (target - mean) / (var + 1.e-6) ** .5
loss = (pred - target) ** 2
loss = loss.mean(dim=-1) # [N, L], mean loss per patch
loss = (loss * mask).sum() / mask.sum() # mean loss on removed patches
return loss
def forward(self, imgs, mask_ratio=0.75):
latent, mask, ids_restore = self.forward_encoder(imgs, mask_ratio)
pred = self.forward_decoder(latent, ids_restore) # [N, L, p*p*3]
loss = self.forward_loss(imgs, pred, mask)
return loss, pred, mask