1. 可以重复选取
给定一个无重复元素的数组 candidates 和一个目标数 target ,找出 candidates 中所有可以使数字和为 target 的组合。 candidates 中的数字可以无限制重复被选取。
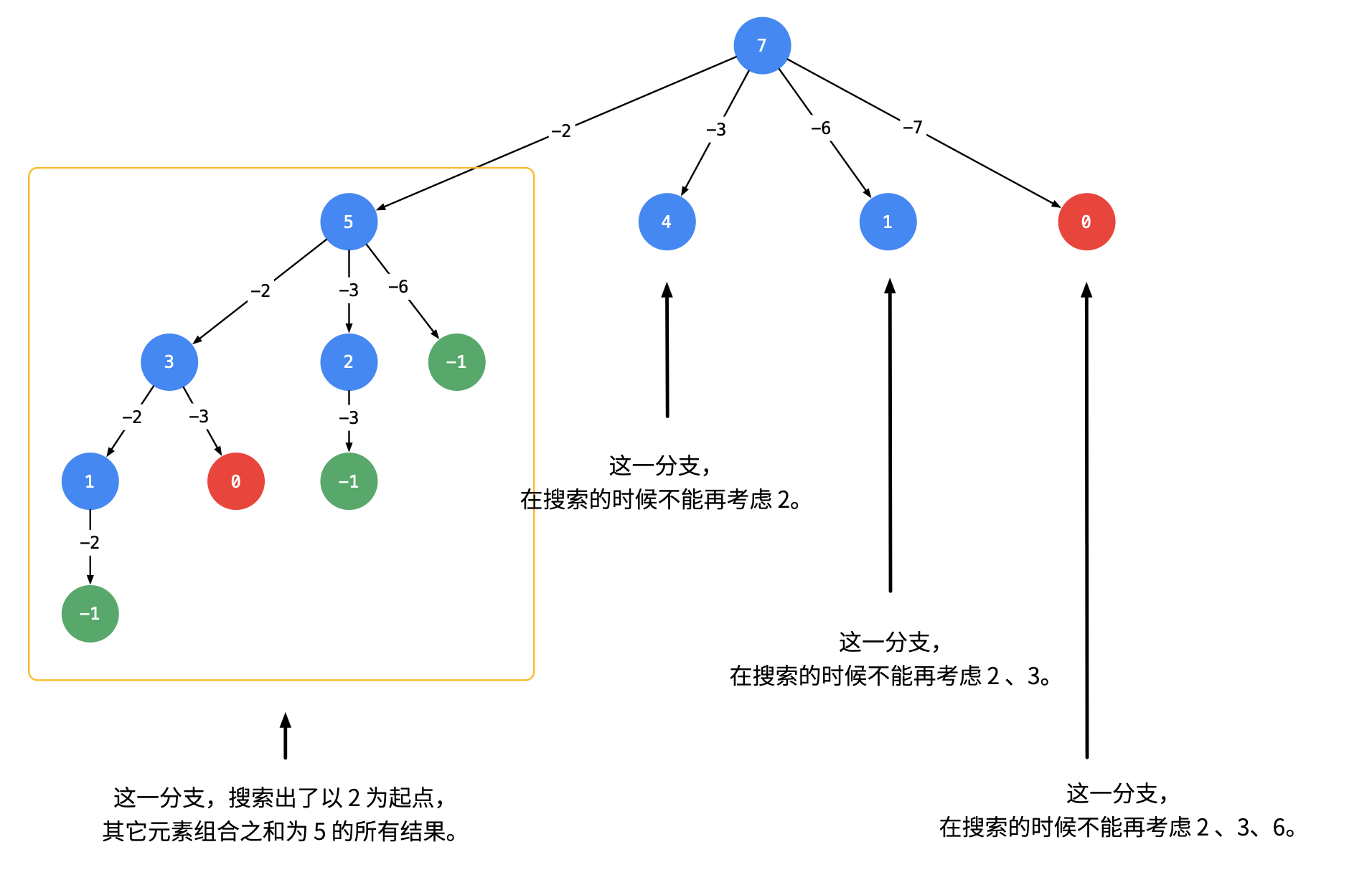
画出树状搜索图如下, 为了去除重复的情况, 我们需要按照某种顺序搜索,具体做法是:每一次搜索的时候,设置下一轮搜索的起点
def combinationSum(self, candidates: List[int], target: int) -> List[List[int]]:
def dfs(candidates, begin, size, path, res, target):
if target == 0:
res.append(path)
return
for index in range(begin, size):
residue = target - candidates[index]
if residue < 0:
break
dfs(candidates, index, size, path + [candidates[index]], res, residue)
size = len(candidates)
if size == 0:
return []
candidates.sort()
path = []
res = []
dfs(candidates, 0, size, path, res, target)
return res
2. 不能被重复选取
与上面的区别在于
- index每次不要重复搜索,而是去寻找下一个
- 排除重复的元素
def combinationSum2(self, candidates: List[int], target: int) -> List[List[int]]: def dfs(begin, path, residue): if residue == 0: res.append(path[:]) return for index in range(begin, size): if candidates[index] > residue: break if index > begin and candidates[index - 1] == candidates[index]: continue # path.append(candidates[index]) dfs(index + 1, path+[candidates[index]], residue - candidates[index]) # path.pop() size = len(candidates) if size == 0: return [] candidates.sort() res = [] dfs(0, [], target) return res